Eribulin Treatment in Patients with Liver Metastatic Breast Cancer: Eight Italian Case Reports
- PMID: 30041178
- PMCID: PMC6193749
- DOI: 10.1159/000489067
Eribulin Treatment in Patients with Liver Metastatic Breast Cancer: Eight Italian Case Reports
Abstract
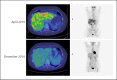
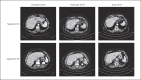
Liver metastases are very common in metastatic breast cancer (MBC); current treatments for these lesions are based on systemic chemotherapy, endocrine- or human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-targeted therapy, and palliative therapy. However, no standard approach has been clearly identified for second and further chemotherapy lines in MBC patients. In the phase III clinical trial EMBRACE, eribulin was particularly effective in reducing liver lesions and improving both overall survival and progression-free survival in liver MBC patients. In this series, we collected 8 case reports of Italian clinical practice in which eribulin has shown significant efficacy in reducing liver metastases in MBC patients: complete response was reported in 2 patients, and 4 patients achieved partial response. The treatment was well tolerated, thus confirming that eribulin is a suitable therapeutic option for elderly patients and for those who have metastatic HER2-negative disease. In the setting of MBC, the sequencing of therapeutic agents should consider expected response, side effects, tumor characteristics, and patient's preferences, in order to successfully tailor the most appropriate therapy beyond earlier lines.
Keywords: Eribulin; Liver metastasis; Metastatic breast cancer; Quality of life.
© 2018 S. Karger AG, Basel.
Figures




References
-
- Ferlay J, Steliarova-Foucher E, Lortet-Tieulent J, Rosso S, Coebergh JWW, Comber H, Forman D, Bray F. Cancer incidence and mortality patterns in Europe: estimates for 40 countries in 2012. Eur J Cancer. 2013;49:1374–1403. - PubMed
-
- Jones SE. Considerations in treatment choice for metastatic breast cancer. Breast Cancer. 2008;15:35–39. - PubMed
-
- Cardoso F, Costa A, Senkus E, Aapro M, André F, Barrios CH, Bergh J, Bhattacharyya G, Biganzoli L, Cardoso MJ, Carey L, Corneliussen-James D, Curigliano G, Dieras V, El Saghir N, Eniu A, Fallowfield L, Fenech D, Francis P, Gelmon K, Gennari A, Harbeck N, Hudis C, Kaufman B, Krop I, Mayer M, Meijer H, Mertz S, Ohno S, Pagani O, Papadopoulos E, Peccatori F, Penault-Llorca F, Piccart MJ, Pierga JY, Rugo H, Shockney L, Sledge G, Swain S, Thomssen C, Tutt A, Vorobiof D, Xu B, Norton L, Winer E. ESO-ESMO 3nd international consensus guidelines for advanced breast cancer (ABC3) Ann Oncol. 2017;28:16–33. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

