Single-cell RNA-seq reveals the diversity of trophoblast subtypes and patterns of differentiation in the human placenta
- PMID: 30042384
- PMCID: PMC6082907
- DOI: 10.1038/s41422-018-0066-y
Single-cell RNA-seq reveals the diversity of trophoblast subtypes and patterns of differentiation in the human placenta
Abstract
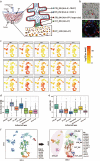
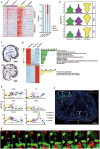
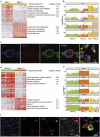
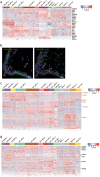
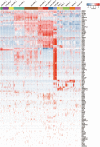
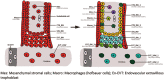
The placenta is crucial for a successful pregnancy and the health of both the fetus and the pregnant woman. However, how the human trophoblast lineage is regulated, including the categorization of the placental cell subtypes is poorly understood. Here we performed single-cell RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) on sorted placental cells from first- and second-trimester human placentas. New subtypes of cells of the known cytotrophoblast cells (CTBs), extravillous trophoblast cells (EVTs), Hofbauer cells, and mesenchymal stromal cells were identified and cell-type-specific gene signatures were defined. Functionally, this study revealed many previously unknown functions of the human placenta. Notably, 102 polypeptide hormone genes were found to be expressed by various subtypes of placental cells, which suggests a complex and significant role of these hormones in regulating fetal growth and adaptations of maternal physiology to pregnancy. These results document human placental trophoblast differentiation at single-cell resolution and thus advance our understanding of human placentation during the early stage of pregnancy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Revealing the molecular landscape of human placenta: a systematic review and meta-analysis of single-cell RNA sequencing studies.Hum Reprod Update. 2024 Jul 1;30(4):410-441. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmae006. Hum Reprod Update. 2024. PMID: 38478759 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation and characterisation of a novel trophoblast side-population from first trimester placentae.Reproduction. 2015 Nov;150(5):449-62. doi: 10.1530/REP-14-0646. Epub 2015 Aug 6. Reproduction. 2015. PMID: 26248480
-
Trophoblast Glycoprotein (TPGB/5T4) in Human Placenta: Expression, Regulation, and Presence in Extracellular Microvesicles and Exosomes.Reprod Sci. 2018 Feb;25(2):185-197. doi: 10.1177/1933719117707053. Epub 2017 May 8. Reprod Sci. 2018. PMID: 28481180 Free PMC article.
-
Human Placental Endothelial Cell and Trophoblast Heterogeneity and Differentiation Revealed by Single-Cell RNA Sequencing.Cells. 2022 Dec 25;12(1):87. doi: 10.3390/cells12010087. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36611882 Free PMC article.
-
New era of trophoblast research: integrating morphological and molecular approaches.Hum Reprod Update. 2020 Sep 1;26(5):611-633. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmaa020. Hum Reprod Update. 2020. PMID: 32728695 Review.
Cited by
-
Paradigms for investigating invasive trophoblast cell development and contributions to uterine spiral artery remodeling.Placenta. 2021 Sep 15;113:48-56. doi: 10.1016/j.placenta.2021.04.012. Epub 2021 May 3. Placenta. 2021. PMID: 33985793 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human archetypal pluripotent stem cells differentiate into trophoblast stem cells via endogenous BMP5/7 induction without transitioning through naive state.Sci Rep. 2024 Feb 8;14(1):3291. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-53381-w. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38332235 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Updates on Research Models and Tools to Study Virus-Host Interactions at the Placenta.Viruses. 2019 Dec 18;12(1):5. doi: 10.3390/v12010005. Viruses. 2019. PMID: 31861492 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Single cell RNA sequencing research in maternal fetal interface.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Jan 10;10:1079961. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.1079961. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 36704195 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The brain-placental axis: Therapeutic and pharmacological relevancy to pregnancy.Pharmacol Res. 2019 Nov;149:104468. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2019.104468. Epub 2019 Oct 7. Pharmacol Res. 2019. PMID: 31600597 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

