Identification of immune-activated hematopoietic stem cells
- PMID: 30042413
- PMCID: PMC6127088
- DOI: 10.1038/s41375-018-0220-z
Identification of immune-activated hematopoietic stem cells
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
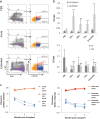
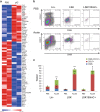
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

