The mutual interplay between calcification and coccolithovirus infection
- PMID: 30043404
- PMCID: PMC7379532
- DOI: 10.1111/1462-2920.14362
The mutual interplay between calcification and coccolithovirus infection
Abstract
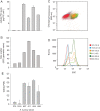
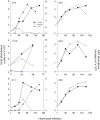
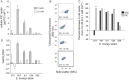
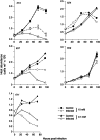
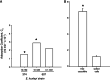
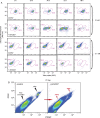
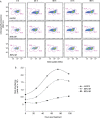
Two prominent characteristics of marine coccolithophores are their secretion of coccoliths and their susceptibility to infection by coccolithoviruses (EhVs), both of which display variation among cells in culture and in natural populations. We examined the impact of calcification on infection by challenging a variety of Emiliania huxleyi strains at different calcification states with EhVs of different virulence. Reduced cellular calcification was associated with increased infection and EhV production, even though calcified cells and associated coccoliths had significantly higher adsorption coefficients than non-calcified (naked) cells. Sialic acid glycosphingolipids, molecules thought to mediate EhV infection, were generally more abundant in calcified cells and enriched in purified, sorted coccoliths, suggesting a biochemical link between calcification and adsorption rates. In turn, viable EhVs impacted cellular calcification absent of lysis by inducing dramatic shifts in optical side scatter signals and a massive release of detached coccoliths in a subpopulation of cells, which could be triggered by resuspension of healthy, calcified host cells in an EhV-free, 'induced media'. Our findings show that calcification is a key component of the E. huxleyi-EhV arms race and an aspect that is critical both to the modelling of these host-virus interactions in the ocean and interpreting their impact on the global carbon cycle.
© 2018 The Authors. Environmental Microbiology published by Society for Applied Microbiology and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures

References
-
- Armstrong, R. A. , Lee, C. , Hedges, J. I. , Honjo, S. , and Wakeham, S. G. (2002) A new, mechanistic model for organic carbon fluxes in the ocean based don the quantitative association of POC with ballast minerals. Deep Sea Res Pt II: Top Stud Oceanogr 49: 219–236.
-
- Balch, W. M. , Kilpatrick, K. A. , Holligan, P. , Harbour, D. , and Fernandez, E. (1996) The 1991 coccolithophore bloom in the Central North Atlantic. 2. Relating optics to coccolith concentration. Limnol Oceanogr 41: 1684–1696.
-
- Balch, W. , D., D , Bowler, W. , and Booth, E. (2007) Prediction of pelagic calcification rates using satellite measurements. Deep Sea Res II: Top Stud Oceanogr 54: 478–495.
-
- Berelson, W. M. , Balch, W. M. , Najiar, R. , Feely, R. A. , Sabine, C. , and Lee, K. (2007) Relating estimates of CaCO3 production, export and dissolution in the water column to measurements of CaCO3 rain into sediment traps and dissolution on the sea floor: a revised global carbonate budget. Global Biogeochem Cycles 21: GB1024.
-
- Berges, J. A. , Franklin, D. J. , and Harrison, P. J. (2001) Evolution of an artificial seawater medium: improvements in enriched seawater, artificial water over the past two decades. J Phycol 37: 1138–1145.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

