Autoimmune hepatitis following influenza virus vaccination: Two case reports
- PMID: 30045302
- PMCID: PMC6078681
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000011621
Autoimmune hepatitis following influenza virus vaccination: Two case reports
Abstract
Rationale: Although immunization could possibly cause autoimmune hepatitis (AIH), to date, no cases of AIH have been reported secondary to influenza virus vaccination. This paper describes 2 women who developed AIH after receiving influenza virus vaccination.
Patient concerns and diagnoses: Two women presented with elevation of liver enzymes after receiving influenza virus vaccination. Both patients were diagnosed with AIH using the International Autoimmune Hepatitis Group criteria.
Intervention and outcomes: Both patients were treated with prednisolone. After the initiation of prednisolone, serum aminotransferase levels were observed to return to the reference range in both patients.
Lessons: Influenza virus vaccination could trigger the development of AIH. Clinicians should be mindful of the fact that AIH can occur after influenza virus vaccination.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

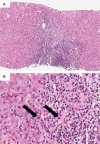
References
-
- Liberal R, Grant CR, Mieli-Vergani G, et al. Autoimmune hepatitis: a comprehensive review. J Autoimmune 2013;41:126–39. - PubMed
-
- Ohira H, Abe K, Takahashi A, et al. Autoimmune hepatitis: recent advances in the pathogenesis and new diagnostic guidelines in Japan. Intern Med 2015;54:1323–8. - PubMed
-
- Czaja AJ, Manns MP. Advances in the diagnosis, pathogenesis, and management of autoimmune hepatitis. Gastroenterology 2010;139:58–72. - PubMed
-
- Vento S, Guella L, Mirandola F, et al. Epstein-Barr virus as a trigger for autoimmune hepatitis in susceptible individuals. Lancet 1995;346:608–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

