"NAD-capQ" detection and quantitation of NAD caps
- PMID: 30045887
- PMCID: PMC6140466
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.067686.118
"NAD-capQ" detection and quantitation of NAD caps
Abstract
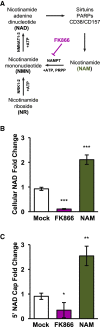
RNA 5' cap structures comprising the metabolic effector nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) have been identified in diverse organisms. Here we report a simple, two-step procedure to detect and quantitate NAD-capped RNA, termed "NAD-capQ." By use of NAD-capQ we quantitate NAD-capped RNA levels in Escherichia coli, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, and human cells, and we measure increases in NAD-capped RNA levels in cells from all three organisms harboring disruptions in their respective "deNADding" enzymes. We further show that NAD-capped RNA levels in human cells respond to changes in cellular NAD concentrations, indicating that NAD capping provides a mechanism for human cells to directly sense and respond to alterations in NAD metabolism. Our findings establish NAD-capQ as a versatile, rapid, and accessible methodology to detect and quantitate 5'-NAD caps on endogenous RNA in any organism.
Keywords: NAD cap; NAD-capQ; mRNA deNADding; mRNA decapping.
© 2018 Grudzien-Nogalska et al.; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press for the RNA Society.
Figures

References
-
- Cahová H, Winz ML, Höfer K, Nübel G, Jäschke A. 2015. NAD captureSeq indicates NAD as a bacterial cap for a subset of regulatory RNAs. Nature 519: 374–377. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
