Start a fire, kill the bug: The role of platelets in inflammation and infection
- PMID: 30049243
- PMCID: PMC6830908
- DOI: 10.1177/1753425918789255
Start a fire, kill the bug: The role of platelets in inflammation and infection
Abstract
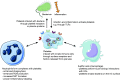
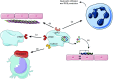
Platelets are the main players in thrombosis and hemostasis; however they also play important roles during inflammation and infection. Through their surface receptors, platelets can directly interact with pathogens and immune cells. Platelets form complexes with neutrophils to modulate their capacities to produce reactive oxygen species or form neutrophil extracellular traps. Furthermore, they release microbicidal factors and cytokines that kill pathogens and influence the immune response, respectively. Platelets also maintain the vascular integrity during inflammation by a mechanism that is different from classical platelet activation. In this review we summarize the current knowledge about how platelets interact with the innate immune system during inflammation and infection and highlight recent advances in the field.
Keywords: Kupffer cell; Platelet; infection; inflammation; macrophages; neutrophils.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures

References
-
- Deppermann C, Kubes P. Platelets and infection. Semin Immunol 2016; 28: 536–545. - PubMed
-
- Ho-Tin-Noé B, Boulaftali Y, Camerer E. Platelets and vascular integrity: How platelets prevent bleeding in inflammation. Blood 2018; 131: 277–288. - PubMed
-
- Deppermann C. Platelets and vascular integrity. Platelets 2018; 00: 1–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

