Randomized control trial evaluation of a modified Paleolithic dietary intervention in the treatment of relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis: a pilot study
- PMID: 30050374
- PMCID: PMC6053098
- DOI: 10.2147/DNND.S116949
Randomized control trial evaluation of a modified Paleolithic dietary intervention in the treatment of relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis: a pilot study
Abstract
Background/objective: A Paleolithic diet may improve fatigue and quality of life in progressive multiple sclerosis (MS) patients, but past research has evaluated the effects of this dietary intervention in combination with other treatments such as exercise. Thus, the purpose of this pilot study was to evaluate a modified Paleolithic dietary intervention (MPDI) in the treatment of fatigue and other symptoms in relapsing-remitting MS (RRMS).
Methods: We measured the effects of a MPDI in 17 individuals with RRMS. Of 34 subjects randomly assigned to control (maintain usual diet) and intervention (MPDI) groups, nine subjects (one man) completed the control group and eight subjects (one man) completed the MPDI.
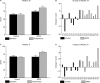
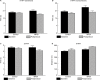
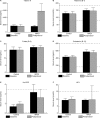
Results: Significant improvements were seen in Fatigue Severity Scale score and also in Multiple Sclerosis Quality of Life-54 and time to complete (dominant hand) 9-Hole Peg Test from baseline in MPDI subjects compared to controls. Increased vitamin K serum levels were also observed in MPDI subjects postprotocol compared to controls.
Conclusion: A Paleolithic diet may be useful in the treatment and management of MS, by reducing perceived fatigue, increasing mental and physical quality of life, increasing exercise capacity, and improving hand and leg function. By increasing vitamin K serum levels, the MPDI may also reduce inflammation.
Keywords: alternative medicine; complementary medicine; diet therapy; fatigue; gluten-free; nutrition therapy; quality of life.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure This study was supported by a grant from TZ Press, which is owned by Dr TLW. Dr TLW has a data management plan on file with The University of Iowa. The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures


References
-
- Ramagopalan SV, Dobson R, Meier UC, Giovannoni G. Multiple sclerosis: risk factors, prodromes, and potential causal pathways. Lancet Neurol. 2010;9(7):727–739. - PubMed
-
- Marrie RA. Environmental risk factors in multiple sclerosis aetiology. Lancet Neurol. 2004;3(12):709–718. - PubMed
-
- Mc Guire C, Prinz M, Beyaert R, van Loo G. Nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kappaB) in multiple sclerosis pathology. Trends Mol Med. 2013;19(10):604–613. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

