A cancer-associated Epstein-Barr virus BZLF1 promoter variant enhances lytic infection
- PMID: 30052684
- PMCID: PMC6082571
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1007179
A cancer-associated Epstein-Barr virus BZLF1 promoter variant enhances lytic infection
Abstract
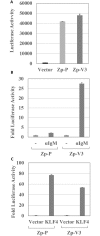
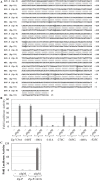
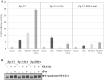
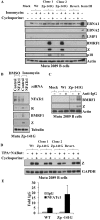
Latent Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection contributes to both B-cell and epithelial-cell malignancies. However, whether lytic EBV infection also contributes to tumors is unclear, although the association between malaria infection and Burkitt lymphomas (BLs) may involve excessive lytic EBV replication. A particular variant of the viral promoter (Zp) that controls lytic EBV reactivation is over-represented, relative to its frequency in non-malignant tissue, in EBV-positive nasopharyngeal carcinomas and AIDS-related lymphomas. To date, no functional differences between the prototype Zp (Zp-P) and the cancer-associated variant (Zp-V3) have been identified. Here we show that a single nucleotide difference between the Zp-V3 and Zp-P promoters creates a binding site for the cellular transcription factor, NFATc1, in the Zp-V3 (but not Zp-P) variant, and greatly enhances Zp activity and lytic viral reactivation in response to NFATc1-inducing stimuli such as B-cell receptor activation and ionomycin. Furthermore, we demonstrate that restoring this NFATc1-motif to the Zp-P variant in the context of the intact EBV B95.8 strain genome greatly enhances lytic viral reactivation in response to the NFATc1-activating agent, ionomycin, and this effect is blocked by the NFAT inhibitory agent, cyclosporine, as well as NFATc1 siRNA. We also show that the Zp-V3 variant is over-represented in EBV-positive BLs and gastric cancers, and in EBV-transformed B-cell lines derived from EBV-infected breast milk of Kenyan mothers that had malaria during pregnancy. These results demonstrate that the Zp-V3 enhances EBV lytic reactivation to physiologically-relevant stimuli, and suggest that increased lytic infection may contribute to the increased prevalence of this variant in EBV-associated malignancies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures





References
-
- Babcock GJ, Decker LL, Volk M, Thorley-Lawson DA. EBV persistence in memory B cells in vivo. Immunity. 1998;9: 395–404. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

