Phase III, randomised trial of avelumab versus physician's choice of chemotherapy as third-line treatment of patients with advanced gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction cancer: primary analysis of JAVELIN Gastric 300
- PMID: 30052729
- PMCID: PMC6225815
- DOI: 10.1093/annonc/mdy264
Phase III, randomised trial of avelumab versus physician's choice of chemotherapy as third-line treatment of patients with advanced gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction cancer: primary analysis of JAVELIN Gastric 300
Abstract
Background: There currently are no internationally recognised treatment guidelines for patients with advanced gastric cancer/gastro-oesophageal junction cancer (GC/GEJC) in whom two prior lines of therapy have failed. The randomised, phase III JAVELIN Gastric 300 trial compared avelumab versus physician's choice of chemotherapy as third-line therapy in patients with advanced GC/GEJC.
Patients and methods: Patients with unresectable, recurrent, locally advanced, or metastatic GC/GEJC were recruited at 147 sites globally. All patients were randomised to receive either avelumab 10 mg/kg by intravenous infusion every 2 weeks or physician's choice of chemotherapy (paclitaxel 80 mg/m2 on days 1, 8, and 15 or irinotecan 150 mg/m2 on days 1 and 15, each of a 4-week treatment cycle); patients ineligible for chemotherapy received best supportive care. The primary end point was overall survival (OS). Secondary end points included progression-free survival (PFS), objective response rate (ORR), and safety.
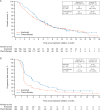
Results: A total of 371 patients were randomised. The trial did not meet its primary end point of improving OS {median, 4.6 versus 5.0 months; hazard ratio (HR)=1.1 [95% confidence interval (CI) 0.9-1.4]; P = 0.81} or the secondary end points of PFS [median, 1.4 versus 2.7 months; HR=1.73 (95% CI 1.4-2.2); P > 0.99] or ORR (2.2% versus 4.3%) in the avelumab versus chemotherapy arms, respectively. Treatment-related adverse events (TRAEs) of any grade occurred in 90 patients (48.9%) and 131 patients (74.0%) in the avelumab and chemotherapy arms, respectively. Grade ≥3 TRAEs occurred in 17 patients (9.2%) in the avelumab arm and in 56 patients (31.6%) in the chemotherapy arm.
Conclusions: Treatment of patients with GC/GEJC with single-agent avelumab in the third-line setting did not result in an improvement in OS or PFS compared with chemotherapy. Avelumab showed a more manageable safety profile than chemotherapy.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov: NCT02625623.
Figures
Comment in
-
Immunotherapy is not for all comers in chemotherapy-refractory advanced gastric cancer. Better predictive biomarkers are needed.Ann Oncol. 2018 Oct 1;29(10):2027-2028. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdy331. Ann Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30137184 No abstract available.
-
Is front-line checkpoint blockade ATTRACTIVE in advanced gastric cancer?Ann Oncol. 2019 Feb 1;30(2):159-161. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdy555. Ann Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30596815 No abstract available.
References
-
- Noone AM, Howlader N, Krapcho M. et al. SEER cancer statistics review, 1975, 2015; https://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2015.
-
- Kang YK, Boku N, Satoh T. et al. Nivolumab in patients with advanced gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction cancer refractory to, or intolerant of, at least two previous chemotherapy regimens (ONO-4538-12, ATTRACTION-2): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2017; 390(10111): 2461–2471. - PubMed
-
- Smyth EC, Verheij M, Allum W. et al. Gastric cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol 2016; 27(Suppl 5): v38–v49. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous