Biosensor-based epitope mapping of antibodies targeting the hemagglutinin and neuraminidase of influenza A virus
- PMID: 30053389
- PMCID: PMC6416777
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jim.2018.07.007
Biosensor-based epitope mapping of antibodies targeting the hemagglutinin and neuraminidase of influenza A virus
Abstract
Characterization of the epitopes on antigen recognized by monoclonal antibodies (mAb) is useful for the development of therapeutic antibodies, diagnostic tools, and vaccines. Epitope mapping also provides functional information for sequence-based repertoire analysis of antibody response to pathogen infection and/or vaccination. However, development of mapping strategies has lagged behind mAb discovery. We have developed a site-directed mutagenesis approach that can be used in conjunction with bio-layer interferometry (BLI) biosensors to map mAb epitopes. By generating a panel of single point mutants in the recombinant hemagglutinin (HA) and neuraminidase (NA) proteins of influenza A viruses, we have characterized the epitopes of hundreds of mAbs targeting the H1 and H3 subtypes of HA and the N9 subtype of NA.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
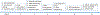
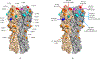

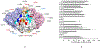
References
-
- Abdiche YN, Lindquist KC, Stone DM, Rajpal A and Pons J, 2012, Label-free epitope binning assays of monoclonal antibodies enable the identification of antigen heterogeneity. J Immunol Methods 382, 101–16. - PubMed
-
- Abdiche YN, Miles A, Eckman J, Foletti D, Van Blarcom TJ, Yeung YA, Pons J and Rajpal A, 2014, High-throughput epitope binning assays on label-free array-based biosensors can yield exquisite epitope discrimination that facilitates the selection of monoclonal antibodies with functional activity. PLoS One 9, e92451. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

