Resolution of synovitis and arrest of catabolic and anabolic bone changes in patients with psoriatic arthritis by IL-17A blockade with secukinumab: results from the prospective PSARTROS study
- PMID: 30053825
- PMCID: PMC6063019
- DOI: 10.1186/s13075-018-1653-5
Resolution of synovitis and arrest of catabolic and anabolic bone changes in patients with psoriatic arthritis by IL-17A blockade with secukinumab: results from the prospective PSARTROS study
Abstract
Background: Although the effects of interleukin-17A (IL-17A) inhibition on the signs and symptoms of psoriatic arthritis (PsA) are well defined, little is known about its impact of local inflammatory and structural changes in the joints. The PSARTROS study was designed to elucidate the effects of IL-17A inhibition on inflammation and bone changes in joints affected by PsA.
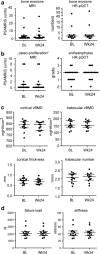
Methods: This was a prospective open-label study in 20 patients with active PsA receiving 24 weeks of treatment with the IL-17A inhibitor secukinumab. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), power Doppler ultrasound (PDUS), and high-resolution peripheral quantitative computer tomography (HR-pQCT) of the hands were performed at baseline and after 24 weeks to assess synovitis, periarticular inflammation, bone erosion, enthesiophyte formation, and bone structure. Demographic and clinical measures of joint disease (DAPSA and DAS28-ESR), skin disease (PASI and BSA), and composite measures (minimal disease activity, or MDA) were also recorded.
Results: Treatment with secukinumab led to significant improvement of signs and symptoms of PsA; 46% reached MDA and 52% DAPSA low disease activity. MRI synovitis (P = 0.034) and signal in PDUS (P = 0.030) significantly decreased after 24 weeks of treatment. Bone erosions in MRI and HR-pQCT and enthesiophytes in the HR-pQCT did not show any progression, and structural integrity and functional bone strength remained stable.
Conclusions: IL-17 inhibition by secukinumab over 24 weeks led to a significant decrease of synovial inflammation and no progression of catabolic and anabolic bone changes in the joints of patients with PsA.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT02483234 , June 26, 2015; retrospectively registered.
Keywords: Bone; Enthesiophytes; Erosions; Psoriatic arthritis; Synovitis; bDMARDs.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
In the PSARTROS study (ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT02483234), all patients provided written informed consent, and institutional review board/ethics committee (Ethik-Kommission der Friedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg) approved the protocol (EC 63_15Az; IRB 2355/01).
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures

References
-
- Ritchlin CT, Colbert RA, Gladman DD. Psoriatic arthritis. N Engl J Med. 2017;376(21):2095–2096. - PubMed
-
- Scher JU, Ubeda C, Artacho A, Attur M, Isaac S, Reddy SM, et al. Decreased bacterial diversity characterizes the altered gut microbiota in patients with psoriatic arthritis, resembling dysbiosis in inflammatory bowel disease. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015;67(1):128–139. doi: 10.1002/art.38892. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

