The Prosigna gene expression assay and responsiveness to adjuvant cyclophosphamide-based chemotherapy in premenopausal high-risk patients with breast cancer
- PMID: 30053900
- PMCID: PMC6062869
- DOI: 10.1186/s13058-018-1012-0
The Prosigna gene expression assay and responsiveness to adjuvant cyclophosphamide-based chemotherapy in premenopausal high-risk patients with breast cancer
Abstract
Background: The PAM50-based (Prosigna) risk of recurrence (ROR) score and intrinsic subtypes are prognostic for women with high-risk breast cancer. We investigate the predictive ability of Prosigna regarding the effectiveness of cyclophosphamide-based adjuvant chemotherapy in premenopausal patients with high-risk breast cancer.
Methods: Prosigna assays were performed on the NanoString platform in tumors from participants in Danish Breast Cancer Group (DBCG) 77B, a four-arm trial that randomized premenopausal women with high-risk early breast cancer to no systemic treatment, levamisole, oral cyclophosphamide (C) or cyclophosphamide, methotrexate and fluorouracil (CMF).
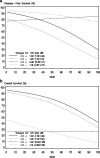
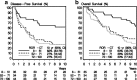
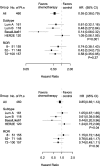
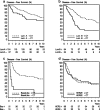
Results: In total, this retrospective analysis included 460 women (40% of the 1146 randomized patients). The continuous Prosigna ROR score was prognostic in the no systemic treatment group (unadjusted P < 0.001 for disease-free survival (DFS), P = 0.001 for overall survival (OS)). No statistically significant interaction of continuous ROR score and treatment on DFS and OS was found. A highly significant association was observed between intrinsic subtypes and C/CMF treatment for DFS (Pinteraction = 0.003 unadjusted, P = 0.001 adjusted) and OS (Pinteraction = 0.04). In the adjusted analysis treatment with C/CMF was associated with a reduced risk of DFS events in patients with basal-like (hazard ratio (HR) 0.14; 95% CI 0.06; 0.32) and luminal B (HR 0.48; 95% CI 0.27; 0.84) subtypes but not in patients with Human epidermal growth factor receptor-enriched (HR 1.05; 95% CI 0.56; 1.95) or luminal A (HR 0.61; 95% CI 0.32; 1.16) subtypes.
Conclusion: The Prosigna ROR score and intrinsic subtypes were prognostic in high-risk premenopausal patients with breast cancer, and intrinsic subtypes identify high-risk patients with or without major benefit from adjuvant C/CMF treatment.
Keywords: Adjuvant chemotherapy; Breast neoplasms; CMF; Cyclophosphamide; PAM50.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The Biomedical Research Ethics Committee of the Danish Capital Region approved the protocol (H-15012740), and granted dispensation from consent.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
MBJ: None. AVL: Nanostring Technologies, Inc.: grant, Roche: grant. TON: Nanostring Technologies, Inc.: personal fees, non-financial support, other: licensing agreement, patent. JOE: none. PW: none. TH: Nanostring Technologies, Inc.: personal fees, other: employee and stock. NR: Nanostring Technologies, Inc.: personal fees: employee. WB: Nanostring Technologies, Inc.: personal fees: employee. SF: Nanostring Technologies, Inc.: other: employee and stock, patent. BE: Nanostring Technologies, Inc:.grant: institutional. Novartis: grant: institutional. Roche: Grant: institutional.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
- Ejlertsen B, Mouridsen HT, Jensen MB, Andersen J, Andersson M, Kamby C, et al. Cyclophosphamide, methotrexate, and fluorouracil; oral cyclophosphamide; levamisole; or no adjuvant therapy for patients with high-risk, premenopausal breast cancer. Cancer. 2010;116(9):2081–2089. - PubMed
-
- Anonymous Adjuvant chemotherapy of breast cancer. NIH consensus development conference, July 14–16, 1980. Cancer Treat Res. 1992;60:371–374. - PubMed
-
- Peto R, Davies C, Godwin J, Gray R, Pan HC, Clarke M, et al. Comparisons between different polychemotherapy regimens for early breast cancer: meta-analyses of long-term outcome among 100,000 women in 123 randomised trials. Lancet. 2012;379:432–444. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)61625-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

