Norovirus devours human milk oligosaccharides rich in α-fucose
- PMID: 30054292
- PMCID: PMC6066310
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.H118.004336
Norovirus devours human milk oligosaccharides rich in α-fucose
Abstract
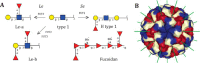
Human norovirus binding to histo-blood group antigens (HBGAs) is thought to direct their entry into host cells. However, the glycan epitopes characteristic of HBGAs are also present on oligosaccharides abundant in human milk. In this issue of JBC, Hanisch et al compared norovirus binding to human gastric mucins and human milk oligosaccharides, finding those bound most avidly are rich in α-fucose. Mimicry of these epitopes with α-fucose multivalently displayed on other carbohydrate scaffolds successfully scavenged this prevalent virus, providing new insights into norovirus biology and clues for future therapeutic development.
© 2018 Krammer and Bouckaert.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

