Interleukin-5, interleukin-6, interferon induced protein-10, procalcitonin and C-reactive protein among mechanically ventilated severe community-acquired viral and bacterial pneumonia patients
- PMID: 30055898
- PMCID: PMC7129555
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cyto.2018.07.019
Interleukin-5, interleukin-6, interferon induced protein-10, procalcitonin and C-reactive protein among mechanically ventilated severe community-acquired viral and bacterial pneumonia patients
Abstract
Background: The serum cytokine levels among 45 mechanically ventilated, intensive care unit (ICU)-treated severe community-acquired pneumonia (SCAP) patients with known microbial etiology in three different etiology groups were assessed.
Methods: Blood samples for C-reactive protein (CRP), procalcitonin (PCT), interleukin (IL)-5, IL-6, IL-10, human interferon gamma induced protein (IP)-10, and TNF-α (tumor necrosis factor alpha) were collected at time points 0, 12, 24, 48, 72 and 96 h after study inclusion.
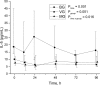
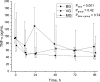
Results: There were 21 (43%) pure bacterial infections (bacterial group, BG), 5 (10%) pure viral infections (viral group, VG), and 19 (39%) mixed bacterial-viral infections (mixed group, MG) among 45 mechanically ventilated SCAP patients. CRP and PCT levels were significantly higher in the MG and values decreased with time in all groups. PCT differed also in time and group analysis (P = 0.001), the highest being in the MG. IL-5 levels were significantly higher in the VG compared to others (Ptime = 0.001, Pgroup = 0.051 and Ptimexgroup = 0.016). IL-6 and IP-10 levels decreased over time (Ptime = 0.003 and Ptime = 0.021), but there were no differences between groups.
Conclusion: SCAP patients with viral etiology have higher IL-5 levels. Patients with mixed viral and bacterial group have higher PCT compared to other etiologies.
Keywords: Cytokine; IL-5; IL-6; IP-10; Pneumonia; Pneumonia etiology; Severe community-acquired pneumonia.
Copyright © 2018 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Mandell L.A., Wunderink R.G., Anzueto A., Bartlett J.G., Campbell G.D., Dean N.C., Dowell S.F., File T.M., Jr, Musher D.M., Niederman M.S., Torres A., Whitney C.G. Infectious diseases society of America/American Thoracic Society consensus guidelines on the management of community-acquired pneumonia in adults. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2007;44:S27–S72. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Choi S.H., Hong S.B., Ko G.B., Lee Y., Park H.J., Park S.Y., Moon S.M., Cho O.H., Park K.H., Chong Y.P., Kim S.H., Huh J.W., Sung H., Do K.H., Lee S.O., Kim M.N., Jeong J.Y., Lim C.M., Kim Y.S., Woo J.H., Koh Y. Viral infection in patients with severe pneumonia requiring intensive care unit admission. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2012;186:325–332. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

