Can 11C-PiB-PET Relative Delivery R1 or 11C-PiB-PET Perfusion Replace 18F-FDG-PET in the Assessment of Brain Neurodegeneration?
- PMID: 30056421
- PMCID: PMC6087437
- DOI: 10.3233/JAD-180274
Can 11C-PiB-PET Relative Delivery R1 or 11C-PiB-PET Perfusion Replace 18F-FDG-PET in the Assessment of Brain Neurodegeneration?
Abstract
Background: Pittsburgh Compound B (PiB) positron emission tomography (PET) is used to visualize in vivo amyloid plaques in the brain. Frequently the PiB examinations are complemented with a fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) PET scan to further assess neurodegeneration.
Objective: Our goal is to identify alternative correlates of FDG images by assessing which kinetic methods originate PiB derived relative delivery ratio (R1) images that can be correlated with the FDG images, and to compare them with PiB perfusion (pPiB) images obtained from the early-phase of PiB acquisition.
Methods: We selected 52 patients with cognitive impairment who underwent a dynamic PiB and FDG acquisitions. To compute the R1 images, two simplified reference tissue models (SRTM and SRTM2) and two multi-linear reference tissue models (MRTM and MRTM2) were used. The pPiB images were obtained in two different time intervals.
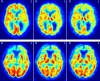
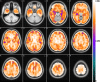
Results: All six types of images were of good quality and highly correlated with the FDG images (mean voxelwise within-subjects r > 0.92). The higher correlation was found for FDG-R1(MRTM). Regarding the voxelwise regional correlation, the higher mean all brain correlations was r = 0.825 for FDG-R1(MRTM) and statistically significant in the whole brain analysis.
Conclusion: All R1 and pPiB images here tested have potential to assess the metabolic impact of neurodegeneration almost as reliably as the FDG images. However, this is not enough to validate these images for a single-subject analysis compared with the FDG image, and thus they cannot yet be used clinically to replace the FDG image before such evaluation.
Keywords: 11C-PIB; 18F-FDG; Alzheimer’s disease; compartmental models; neurodegeneration; perfusion.
Figures


References
-
- Hardy J, Selkoe DJ (2002) The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease: Progress and problems on the road to therapeutics. Science 297, 353–356. - PubMed
-
- Meyer PT, Hellwig S, Amtage F, Rottenburger C, Sahm U, Reuland P, Weber WA, Hüll M (2011) Dual-biomarker imaging of regional cerebral amyloid load and neuronal activity in dementia with PET and 11C-labeled Pittsburgh compound B. J Nucl Med 52, 393–400. - PubMed
-
- Rodriguez-Vieitez E, Carter SF, Chiotis K, Saint-Aubert L, Leuzy A, Schöll M, Almkvist O, Wall A, Långström B, Nordberg A (2016) Comparison of early-phase 11C-Deuterium-L-Deprenyl and 11C-PiB PET for assessing brain perfusion in Alzheimer’s disease. J Nucl Med 57, 1071–1077. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

