A comparison of qPCR and ddPCR used for quantification of the JAK2 V617F allele burden in Ph negative MPNs
- PMID: 30056580
- PMCID: PMC6208664
- DOI: 10.1007/s00277-018-3451-1
A comparison of qPCR and ddPCR used for quantification of the JAK2 V617F allele burden in Ph negative MPNs
Abstract
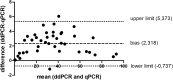
Philadelphia-negative myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs) are a diverse group of diseases whose common feature is the presence of V617F mutation of the JAK2 gene. In the era of novel therapeutic strategies in MPNs, such as JAK-inhibitor therapy, there is a growing need for establishing high sensitive quantitative methods, which can be useful not only at diagnosis but also for monitoring therapeutic outcomes, such as minimal residual disease (MRD). In this study, we compared the qPCR and ddPCR methods and their clinical utility for diagnosis, prognostication, and treatment monitoring of MPNs with JAK2 V617F mutation in 63 MPN patients of which 6 were subjected to ruxolitinib treatment. We show a high conformance between the two methods (correlation coefficient r = 0.998 (p < 0.0001)). Our experiments revealed high analytical sensitivity for both tests, suggesting that they are capable of detecting the JAK2 V617F mutation at diagnosis of MPN with a limit of detection (LoD) of 0.12% for qPCR and 0.01% for ddPCR. The alterations of JAK2 V617F allele burden in patients treated with ruxolitinib were measured by both methods with equal accuracy. The results suggest an advantage of ddPCR in monitoring MRD because of allele burdens below the LoD of qPCR. Overall, the clinical utility of qPCR and ddPCR is very high, and both methods could be recommended for the routine detection of the V617F mutation at diagnosis, though ddPCR will probably supersede qPCR in the future due to cost-effectiveness.
Keywords: JAK-inhibitor; Limit of detection; Minimal residual disease; Myeloproliferative neoplasms; ddPCR; qPCR.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

