NonA and CPX Link the Circadian Clockwork to Locomotor Activity in Drosophila
- PMID: 30057203
- PMCID: PMC6442453
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2018.07.001
NonA and CPX Link the Circadian Clockwork to Locomotor Activity in Drosophila
Abstract
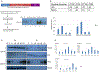
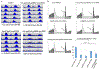
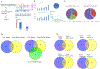
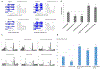
Drosophila NonA and its mammalian ortholog NONO are members of the Drosophila behavior and human splicing (DBHS) family. NONO also has a strong circadian connection: it associates with the circadian repressor protein PERIOD (PER) and contributes to circadian timekeeping. Here, we investigate NonA, which is required for proper levels of evening locomotor activity as well as a normal free-running period in Drosophila. NonA is associated with the positive transcription factor CLOCK/CYCLE (CLK/CYC), interacts directly with complexin (cpx) pre-mRNA, and upregulates gene expression, including the gene cpx. Downregulation of cpx expression in circadian neurons phenocopies NonA downregulation, whereas cpx overexpression rescues the nonA RNAi phenotypes, indicating that cpx is an important NonA target gene. As the cpx protein contributes to proper neurotransmitter and neuropeptide release in response to calcium, these results and others indicate that this control is important for the normal circadian regulation of locomotor activity.
Keywords: CLOCK; CPX; Drosophila; NonA; PDF; circadian rhythm; neuropeptide; neurotransmitter; vesicle release.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests:
The Authors declare that there are no conflicts of interests.
Figures


References
-
- Abruzzi K, Chen X, Nagoshi E, Zadina A, and Rosbash M (2015). RNA-seq Profiling of Small Numbers of Drosophila Neurons. Methods Enzymol 551, 369–386. - PubMed
-
- Amelio AL, Miraglia LJ, Conkright JJ, Mercer BA, Batalov S, Cavett V, Orth AP, Busby J, Hogenesch JB, and Conkright MD (2007). A coactivator trap identifies NONO (p54nrb) as a component of the cAMP-signaling pathway. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 104, 20314–20319. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

