Acute pulmonary embolism: endovascular therapy
- PMID: 30057873
- PMCID: PMC6039803
- DOI: 10.21037/cdt.2017.12.05
Acute pulmonary embolism: endovascular therapy
Abstract
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide. PE is a complex disease with a highly variable presentation and the available treatment options for PE are expanding rapidly. Anticoagulation (AC), systemic lysis, surgery, and catheter-directed thrombolysis (CDT) play important roles in treating patients with PE. Thus, a multidisciplinary approach to diagnosis, risk stratification, and therapy is required to determine which treatment option is best for a given patient with this complex disease.
Keywords: Pulmonary embolism (PE); interdisciplinary communication; mechanical thrombolysis; thrombolytic therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: AK Sista received research grant from Penumbra, Inc., administered through NYU Department of Radiology, and he is an unpaid scientific advisory board member of Thrombolex. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
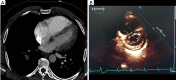
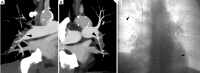


References
-
- Provias T, Dudzinski DM, Jaff MR, et al. The Massachusetts General Hospital Pulmonary Embolism Response Team (MGH PERT): creation of a multidisciplinary program to improve care of patients with massive and submassive pulmonary embolism. Hosp Pract (1995) 2014;42:31-7. 10.3810/hp.2014.02.1089 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
