Immunogenomics Analysis Reveals that TP53 Mutations Inhibit Tumor Immunity in Gastric Cancer
- PMID: 30059832
- PMCID: PMC6078052
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tranon.2018.07.012
Immunogenomics Analysis Reveals that TP53 Mutations Inhibit Tumor Immunity in Gastric Cancer
Abstract
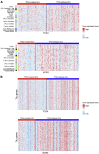
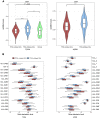
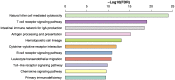
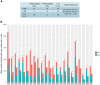
Although immunotherapy continues to demonstrate efficacy in a variety of refractory cancers, currently, no any immunotherapeutic strategy is clinically used for gastric cancer (GC) except its microsatellite instable subtype. Thus, it is important to identify molecular biomarkers for predicting the responders to GC immunotherapy. TP53 mutations frequently occur in GC and are associated with unfavorable clinical outcomes in GC. We performed a comprehensive characterization of the associations between TP53 mutations and immune activities in GC based on two large-scale GC cancer genomics data. We compared expression and enrichment levels of 787 immune-related genes and 23 immune gene-sets among TP53-mutated GCs, TP53-wildtype GCs, and normal tissue, and explored the correlations between p53-mediated pathways and immune activities in GC. Strikingly, almost all analyzed immune gene-sets were significantly downregulated in enrichment levels in TP53-mutated GCs compared to TP53-wildtype GCs. These less active immune pathways and cell types in TP53-mutated GCs included 15 immune cell types and function, tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes, regulatory T cells, immune checkpoint, cytokine and cytokine receptor, human leukocyte antigen, pro-inflammatory, and parainflammation. Moreover, we identified a number of p53-mediated pathways and proteins that were significantly associated with immune activities in GC. Furthermore, we demonstrated that the TP53 mutation itself could result in the depressed immune activities in GC and other cancer types. We revealed that chromosomal instability was an important mechanism for the depressed tumor immunity in TP53-mutated cancers. Finally, we showed that immune cell infiltration and immune activities were likely positively associated with survival prognosis in GC. Our findings suggest that p53 may play an important role in activating tumor immunity in GC and other cancer types and that the TP53 mutation status could be useful in stratifying cancer patients responsive to a certain immunotherapy.
Copyright © 2018 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Correlate the TP53 Mutation and the HRAS Mutation with Immune Signatures in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Cancer.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2019 Jul 26;17:1020-1030. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2019.07.009. eCollection 2019. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2019. PMID: 31428295 Free PMC article.
-
Cancer type-dependent correlations between TP53 mutations and antitumor immunity.DNA Repair (Amst). 2020 Apr;88:102785. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2020.102785. Epub 2020 Jan 24. DNA Repair (Amst). 2020. PMID: 32007736
-
TP53 Mutations Promote Immunogenic Activity in Breast Cancer.J Oncol. 2019 Jun 2;2019:5952836. doi: 10.1155/2019/5952836. eCollection 2019. J Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31275382 Free PMC article.
-
p53 in breast cancer subtypes and new insights into response to chemotherapy.Breast. 2013 Aug;22 Suppl 2:S27-9. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2013.07.005. Breast. 2013. PMID: 24074787 Review.
-
[TP53 mutations and molecular epidemiology].Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. 2007 May;34(5):683-9. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. 2007. PMID: 17496437 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
A biopsy-based Immunoscore in patients with treatment-naïve resectable gastric cancer.Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2024 Oct 21;16:17588359241287747. doi: 10.1177/17588359241287747. eCollection 2024. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39444424 Free PMC article.
-
Isoforms of the p53 Family and Gastric Cancer: A Ménage à Trois for an Unfinished Affair.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Feb 22;13(4):916. doi: 10.3390/cancers13040916. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33671606 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulation of BCL-2 in Both T Cells and Tumor Cells to Enhance Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-cell Immunotherapy against Cancer.Cancer Discov. 2022 Oct 5;12(10):2372-2391. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-21-1026. Cancer Discov. 2022. PMID: 35904479 Free PMC article.
-
Reactivation of mutant p53 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by isothiocyanate inhibits tumor growth.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Apr 24;14:1141420. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1141420. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37168998 Free PMC article.
-
Gene set enrichment analysis identifies immune subtypes of kidney renal clear cell carcinoma with significantly different molecular and clinical properties.Front Immunol. 2023 Jun 23;14:1191365. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1191365. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37426638 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zitvogel L, Kroemer G. CANCER. A p53-regulated immune checkpoint relevant to cancer. Science. 2015;349(6247):476–477. - PubMed
-
- Textor S, Fiegler N, Arnold A, Porgador A, Hofmann TG, Cerwenka A. Human NK cells are alerted to induction of p53 in cancer cells by upregulation of the NKG2D ligands ULBP1 and ULBP2. Cancer Res. 2011;71(18):5998–6009. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

