Multiple Instances QoS Routing in RPL: Application to Smart Grids
- PMID: 30061544
- PMCID: PMC6111979
- DOI: 10.3390/s18082472
Multiple Instances QoS Routing in RPL: Application to Smart Grids
Abstract
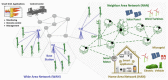
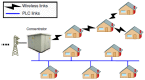
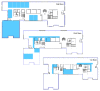
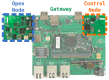
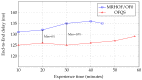
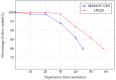
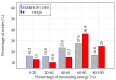
The Smart Grid (SG) aims to transform the current electric grid into a "smarter" network where the integration of renewable energy resources, energy efficiency and fault tolerance are the main benefits. This is done by interconnecting every energy source, storage point or central control point with connected devices, where heterogeneous SG applications and signalling messages will have different requirements in terms of reliability, latency and priority. Hence, data routing and prioritization are the main challenges in such networks. So far, RPL (Routing Protocol for Low-Power and Lossy networks) protocol is widely used on Smart Grids for distributing commands over the grid. RPL assures traffic differentiation at the network layer in wireless sensor networks through the logical subdivision of the network in multiple instances, each one relying on a specific Objective Function. However, RPL is not optimized for Smart Grids, as its main objective functions and their associated metric does not allow Quality of Service differentiation. To overcome this, we propose OFQS an objective function with a multi-objective metric that considers the delay and the remaining energy in the battery nodes alongside with the dynamic quality of the communication links. Our function automatically adapts to the number of instances (traffic classes) providing a Quality of Service differentiation based on the different Smart Grid applications requirements. We tested our approach on a real sensor testbed. The experimental results show that our proposal provides a lower packet delivery latency and a higher packet delivery ratio while extending the lifetime of the network compared to solutions in the literature.
Keywords: QoS; RPL; Smart Grid; WSN; metric; objective function; routing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Bouhafs F., Mackay M., Merabti M. Links to the future: Communication requirements and challenges in the smart grid. IEEE Power Energy Mag. 2012;10:24–32. doi: 10.1109/MPE.2011.943134. - DOI
-
- Gungor V.C., Lu B., Hancke G.P. Opportunities and challenges of wireless sensor networks in smart grid. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2010;57:3557–3564. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2009.2039455. - DOI
-
- BKW . Smart Grid Taxonomy. A System View From a Grid Operator’s Perspective. BKW; Bern, Switzerland: 2015. version 2.0 beta.
-
- Davito B., Tai H., Uhlaner R. The smart grid and the promise of demand-side management. McKinsey Smart Grid. 2010;3:8–44.
-
- Rekik M. Ph.D. Thesis. Université Lille 1; Villeneuve-d’Ascq, France: 2016. Routage GéOgraphique Multi-Chemin Basé Sur L’Intelligence D’Essaim Pour RéSeaux de Capteurs Et D’Actionneurs Sans Fil: Application Aux Smart Grids.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

