Application of nSMOL coupled with LC-MS bioanalysis for monitoring the Fc-fusion biopharmaceuticals Etanercept and Abatacept in human serum
- PMID: 30062014
- PMCID: PMC6056752
- DOI: 10.1002/prp2.422
Application of nSMOL coupled with LC-MS bioanalysis for monitoring the Fc-fusion biopharmaceuticals Etanercept and Abatacept in human serum
Abstract
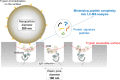
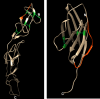
The principle of nano-surface and molecular-orientation limited (nSMOL) proteolysis has a unique characteristic Fab-selective proteolysis for antibody bioanalysis that is independent of a variety of monoclonal antibodies by the binding antibody Fc via Protein A/G in a pore with 100 nm diameter and modified trypsin immobilization on the surface of nanoparticles with 200 nm diameter. Since minimizing peptide complexity and protease contamination while maintaining antibody sequence specificity enables a rapid and broad development of optimized methods for liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) bioanalysis, the application of regulatory LC-MS for monitoring antibody biopharmaceuticals is expected. nSMOL is theoretically anticipated to be applicable for representative Fc-fusion biopharmaceuticals, because Protein A/G-binding site Fc exists on the C-terminus, and its functional domain is available to orient and interact with the reaction solution. In this report, we describe the validated LC-MS bioanalysis for monitoring Ethanercept and Abatacept using nSMOL technology. The quantitation range of Ethanercept in human serum was from 0.195 to 100 μg/mL using the signature peptide VFCTK (aa.43-47), and that of Abatacept was from 0.391 to 100 μg/mL using the signature peptide MHVAQPAVVLASSR (aa.1-14). Both proteins fulfilled the guideline criteria for low-molecular-weight drug compounds. The results indicate that the clinical and therapeutic monitoring for antibody and Fc-fusion biopharmaceuticals are adequately applicable using nSMOL proteolysis coupled with LC-MS bioanalysis.
Keywords: Abatacept; Etanercept; LC‐MS; bioanalysis; clinical pharmacokinetics; nano‐surface and molecular‐orientation limited proteolysis; therapeutic drug monitoring.
Figures

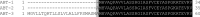
References
-
- Suffredini AF, Reda D, Banks SM, Tropea M, Agosti JM, Miller R. Effects of recombinant dimeric TNF receptor on human inflammatory responses following intravenous endotoxin administration. J Immunol. 1995;155:5038‐5045. - PubMed
-
- Epstein WV. Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with a tumor necrosis factor receptor‐Fc fusion protein. N Engl J Med. 1997;337:1559‐1560; author reply 60‐1. - PubMed
-
- Favalli EG, Pontikaki I, Becciolini A, et al. Real‐life 10‐year retention rate of first‐line anti‐TNF drugs for inflammatory arthritides in adult‐ and juvenile‐onset populations: similarities and differences. Clin Rheumatol. 2017;36:1747‐1755. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

