Tuberculous Orchitis Following Intravesical Bacille Calmette-Guérin (BCG) Therapy
- PMID: 30062077
- PMCID: PMC6063386
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.2703
Tuberculous Orchitis Following Intravesical Bacille Calmette-Guérin (BCG) Therapy
Abstract
Intravesical therapy with Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) is a common and effective therapy for bladder carcinoma in situ. The risks associated with intravesical BCG therapy are significant and rare. Accurate diagnosis and prompt initiation of management significantly reduce the morbidity associated with these risks. Here, we discuss a case of BCG orchitis, a rare but treatable complication of intravesical BCG therapy. We present the case of a 55-year-old Puerto Rican incarcerated male who was diagnosed with high-grade Stage T1 urothelial carcinoma after presenting with hematuria, treated with transurethral resection of bladder tumor (TURBT), mitomycin, and intravesical BCG. He presented with left testicular pain and swelling after a failed course of ciprofloxacin with ultrasound findings characteristic of BCG orchitis. The patient received a combination therapy of levofloxacin, rifampin, isoniazid, and ethambutol, which resulted in symptom resolution. Combination therapy was initiated in this patient based on a high index of clinical suspicion, and in the absence of positive cultures. Competing diagnoses were considered and excluded based on the history, imaging findings, and observed response to therapy. As this is an uncommon diagnosis, and as routine infectious workup is often inconclusive, we emphasize that early anti-tuberculous treatment should be considered given a high degree of clinical suspicion based on history and patient presentation.
Keywords: bacillus calmette-guerin (bcg); bcg orchitis; bladder cancer; ethambutol; isoniazid; levofloxacin; rifampin; testicular ultrasound; tuberculosis; tuberculous orchitis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
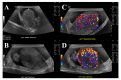
References
-
- Diagnosis and treatment of non-muscle invasive bladder cancer: AUA/SUO guideline. Chang SS, Boorjian SA, Chou R, et al. J Urol. 2016;196:1021–1029. - PubMed
-
- Guidelines on bladder cancer. Oosterlinck W, Lobel B, Jakse G, et al. Eur Urol. 2002;41:105–112. - PubMed
-
- Efficacy and safety of bacille Calmette-Guerin immunotherapy in superficial bladder cancer. Lamm DL. Clin Infect Dis. 2000;31:0. - PubMed
-
- Bacillus Calmette-Guerin (BCG) infection following intravesical BCG administration as adjunctive therapy for bladder cancer: incidence, risk factors, and outcome in a single-institution series and review of the literature. Pérez-Jacoiste Asín MA, Fernández-Ruiz M, López-Medrano F, et al. Medicine (Baltimore) 2014;93:236–254. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
