Deep Learning Approach for Evaluating Knee MR Images: Achieving High Diagnostic Performance for Cartilage Lesion Detection
- PMID: 30063195
- PMCID: PMC6166867
- DOI: 10.1148/radiol.2018172986
Deep Learning Approach for Evaluating Knee MR Images: Achieving High Diagnostic Performance for Cartilage Lesion Detection
Abstract
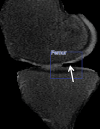
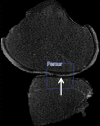
Purpose To determine the feasibility of using a deep learning approach to detect cartilage lesions (including cartilage softening, fibrillation, fissuring, focal defects, diffuse thinning due to cartilage degeneration, and acute cartilage injury) within the knee joint on MR images. Materials and Methods A fully automated deep learning-based cartilage lesion detection system was developed by using segmentation and classification convolutional neural networks (CNNs). Fat-suppressed T2-weighted fast spin-echo MRI data sets of the knee of 175 patients with knee pain were retrospectively analyzed by using the deep learning method. The reference standard for training the CNN classification was the interpretation provided by a fellowship-trained musculoskeletal radiologist of the presence or absence of a cartilage lesion within 17 395 small image patches placed on the articular surfaces of the femur and tibia. Receiver operating curve (ROC) analysis and the κ statistic were used to assess diagnostic performance and intraobserver agreement for detecting cartilage lesions for two individual evaluations performed by the cartilage lesion detection system. Results The sensitivity and specificity of the cartilage lesion detection system at the optimal threshold according to the Youden index were 84.1% and 85.2%, respectively, for evaluation 1 and 80.5% and 87.9%, respectively, for evaluation 2. Areas under the ROC curve were 0.917 and 0.914 for evaluations 1 and 2, respectively, indicating high overall diagnostic accuracy for detecting cartilage lesions. There was good intraobserver agreement between the two individual evaluations, with a κ of 0.76. Conclusion This study demonstrated the feasibility of using a fully automated deep learning-based cartilage lesion detection system to evaluate the articular cartilage of the knee joint with high diagnostic performance and good intraobserver agreement for detecting cartilage degeneration and acute cartilage injury. © RSNA, 2018 Online supplemental material is available for this article .
Figures





References
-
- Fransen M, McConnell S. Land-based exercise for osteoarthritis of the knee: a metaanalysis of randomized controlled trials. J Rheumatol 2009;36(6):1109–1117. - PubMed
-
- Le Hellio. Graverand-Gastineau MP. OA clinical trials: current targets and trials for OA. Choosing molecular targets: what have we learned and where we are headed? Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2009;17(11):1393–1401. - PubMed
-
- Hunter DJ, Hellio Le Graverand-Gastineau MP. How close are we to having structure-modifying drugs available? Rheum Dis Clin North Am 2008;34(3):789–802. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

