HSRA: Hadoop-based spliced read aligner for RNA sequencing data
- PMID: 30063721
- PMCID: PMC6067734
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0201483
HSRA: Hadoop-based spliced read aligner for RNA sequencing data
Abstract
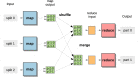
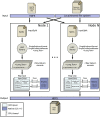
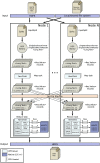
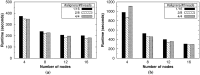
Nowadays, the analysis of transcriptome sequencing (RNA-seq) data has become the standard method for quantifying the levels of gene expression. In RNA-seq experiments, the mapping of short reads to a reference genome or transcriptome is considered a crucial step that remains as one of the most time-consuming. With the steady development of Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) technologies, unprecedented amounts of genomic data introduce significant challenges in terms of storage, processing and downstream analysis. As cost and throughput continue to improve, there is a growing need for new software solutions that minimize the impact of increasing data volume on RNA read alignment. In this work we introduce HSRA, a Big Data tool that takes advantage of the MapReduce programming model to extend the multithreading capabilities of a state-of-the-art spliced read aligner for RNA-seq data (HISAT2) to distributed memory systems such as multi-core clusters or cloud platforms. HSRA has been built upon the Hadoop MapReduce framework and supports both single- and paired-end reads from FASTQ/FASTA datasets, providing output alignments in SAM format. The design of HSRA has been carefully optimized to avoid the main limitations and major causes of inefficiency found in previous Big Data mapping tools, which cannot fully exploit the raw performance of the underlying aligner. On a 16-node multi-core cluster, HSRA is on average 2.3 times faster than previous Hadoop-based tools. Source code in Java as well as a user's guide are publicly available for download at http://hsra.dec.udc.es.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



Similar articles
-
MarDRe: efficient MapReduce-based removal of duplicate DNA reads in the cloud.Bioinformatics. 2017 Sep 1;33(17):2762-2764. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btx307. Bioinformatics. 2017. PMID: 28475668
-
RNA-Seq read alignments with PALMapper.Curr Protoc Bioinformatics. 2010 Dec;Chapter 11:Unit 11.6. doi: 10.1002/0471250953.bi1106s32. Curr Protoc Bioinformatics. 2010. PMID: 21154708
-
Parallel and Scalable Short-Read Alignment on Multi-Core Clusters Using UPC+.PLoS One. 2016 Jan 5;11(1):e0145490. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0145490. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26731399 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping RNA-seq Reads with STAR.Curr Protoc Bioinformatics. 2015 Sep 3;51:11.14.1-11.14.19. doi: 10.1002/0471250953.bi1114s51. Curr Protoc Bioinformatics. 2015. PMID: 26334920 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Applications of the MapReduce programming framework to clinical big data analysis: current landscape and future trends.BioData Min. 2014 Oct 29;7:22. doi: 10.1186/1756-0381-7-22. eCollection 2014. BioData Min. 2014. PMID: 25383096 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Integrated Genome and Transcriptome Sequencing to Solve a Neuromuscular Puzzle: Miyoshi Muscular Dystrophy and Early Onset Primary Dystonia in Siblings of the Same Family.Front Genet. 2021 Jul 2;12:672906. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.672906. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34276779 Free PMC article.
-
BigFiRSt: A Software Program Using Big Data Technique for Mining Simple Sequence Repeats From Large-Scale Sequencing Data.Front Big Data. 2022 Jan 18;4:727216. doi: 10.3389/fdata.2021.727216. eCollection 2021. Front Big Data. 2022. PMID: 35118375 Free PMC article.
-
SparkEC: speeding up alignment-based DNA error correction tools.BMC Bioinformatics. 2022 Nov 7;23(1):464. doi: 10.1186/s12859-022-05013-1. BMC Bioinformatics. 2022. PMID: 36344928 Free PMC article.
-
Cloud accelerated alignment and assembly of full-length single-cell RNA-seq data using Falco.BMC Genomics. 2019 Dec 30;20(Suppl 10):927. doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-6341-6. BMC Genomics. 2019. PMID: 31888474 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dean J, Ghemawat S. MapReduce: simplified data processing on large clusters. Commun ACM. 2008;51(1):107–113. 10.1145/1327452.1327492 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

