MALDI-TOF MS monitoring of PBMC activation status in sepsis
- PMID: 30064357
- PMCID: PMC6069833
- DOI: 10.1186/s12879-018-3266-7
MALDI-TOF MS monitoring of PBMC activation status in sepsis
Abstract
Background: MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry (MS) on whole cells enables the detection of different cell types and cell activation. Here, we wondered whether this approach would be useful to investigate the host response in sepsis.
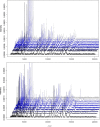
Methods: Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from patients with severe sepsis and healthy donors were analyzed with MALDI-TOF MS. PBMCs from healthy donors were also stimulated with lipopolysaccharide, peptidoglycan, CpG oligonucleotides, polyinosinic polycytidylic acid, and with heat-inactivated bacteria. Averaged spectra of PBMCs stimulated in vitro by different agonists were generated from the database using the Biotyper software and matching scores between each spectrum from patients and averaged spectra from the database were calculated.
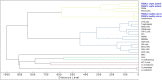
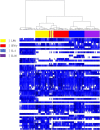
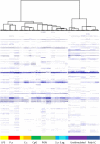
Results: We show that the MALDI-TOF MS signature of PBMCs from septic patients was specific, compared with healthy controls. As the fingerprints observed in patients may be related to PBMC activation, PBMCs from healthy controls were stimulated with cytokines, soluble Pathogen-Associated Molecular Patterns (PAMPs) and heat-killed bacteria, and we created a database of reference spectra. The MALDI-TOF MS profiles of PBMCs from septic patients were then compared with the database. No differences were found between patients with documented infection (n = 6) and those without bacteriological documentation (n = 6). The spectra of PBMCs from septic patients matched with those of interferon-γ- and interleukin-10-stimulated PBMCs, confirming that sepsis is characterized by both inflammatory and immunoregulatory features. Interestingly, the spectra of PBMCs from septic patients without documented infection matched with the reference spectrum of PBMCs stimulated by CpG oligonucleotides, suggesting a bacterial etiology in these patients.
Conclusions: Despite the limits of this preliminary study, these results indicate that the monitoring of functional status of PBMCs in peripheral blood by whole cell MALDI-TOF MS could provide unique opportunities to assess disease progression or resolution in clinical settings.
Keywords: CpG oligonucleotides; IFN-γ; Interleukin-10; MALDI-TOF; Mass spectrometry; Mononuclear cells; Sepsis.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Patient recruitment was provided from an ancillary study to the project “De-escalation of Empirical Antibiotics in Severe Sepsis”. Written informed consent was obtained from the participants or their parents. The study was approved by the Ethics Committee Sud Méditerranée (No. 2011–002297-22). Confidentiality of the participants’ details was assured.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures

References
-
- Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour CW, Shankar-Hari M, Annane D, Bauer M, Bellomo R, Bernard GR, Chiche JD, Coopersmith CM, Hotchkiss RS, Levy MM, Marshall JC, Martin GS, Opal SM, Rubenfeld GD, van der Poll T, Vincent JL, Angus DC. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3) JAMA. 2016;315:801–810. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.0287. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dellinger RP, Levy MM, Rhodes A, Annane D, Gerlach H, Opal SM, Sevransky JE, Sprung CL, Douglas IS, Jaeschke R, Osborn TM, Nunnally ME, Townsend SR, Reinhart K, Kleinpell RM, Angus DC, Deutschman CS, Machado FR, Rubenfeld GD, Webb S, Beale RJ, Vincent JL, Moreno R, Surviving Sepsis Campaign Guidelines Committee including The Pediatric Subgroup Surviving Sepsis Campaign: international guidelines for management of severe sepsis and septic shock, 2012. Intensive Care Med. 2013;39:165–228. doi: 10.1007/s00134-012-2769-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Adrie C, Alberti C, Chaix-Couturier C, Azoulay E, De Lassence A, Cohen Y, Meshaka P, Cheval C, Thuong M, Troché G, Garrouste-Orgeas M, Timsit JF. Epidemiology and economic evaluation of severe sepsis in France: age, severity, infection site, and place of acquisition (community, hospital, or intensive care unit) as determinants of workload and cost. J Crit Care. 2005;20:46–58. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrc.2004.10.005. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

