Validation of insulin-like growth factor-1 as a prognostic parameter in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma in a European cohort
- PMID: 30064393
- PMCID: PMC6069541
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-018-4677-y
Validation of insulin-like growth factor-1 as a prognostic parameter in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma in a European cohort
Abstract
Background: In hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the third leading cause of cancer-related mortality worldwide, the Child-Turcotte-Pugh score (CTP) is one of the most established tools to assess hepatic reserve and determine survival. Serum levels of insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) are decreased in patients with chronic liver disease or HCC. A modified score combining circulating IGF-1 with the CTP score (IGF-CTP) was recently proposed.
Methods: IGF-CTP scoring was evaluated in 216 patients diagnosed with HCC between 2007 and 2017 to assess the predictive value of serum IGF-1 levels for patient risk stratification and overall survival (OS).
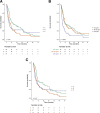
Results: Liver cirrhosis was identified in 80.1% of the study cohort, and alcohol-induced liver disease was the most frequent underlying cause of HCC (44.4%). Serum IGF-1 levels were significantly lower in patients with HCC in cirrhosis compared with non-cirrhotic HCC (p < 0.01). A lower serum level of IGF-1 was associated with more advanced stages of liver cirrhosis (p < 0.05) and cancer stages (p < 0.001). Median OS in the cohort was 11.4 months (range 0.5-118.2 months). OS was significantly higher (10.9 vs. 7.9 months; p < 0.05) in patients with a serum IGF-1 level above the median of 43.4 ng/mL. Patient reassignment using IGF-CTP scoring reclassified 35.6% of patients. Through reassignment, stratification regarding OS was comparable to CTP.
Conclusions: This study is the first to investigate IGF-1 and the IGF-CTP classification in a European cohort of HCC patients. Serum IGF-1 correlates with OS in patients with HCC. However, the IGF-CTP classification was not superior compared to CTP score regarding OS.
Keywords: Clinical database; HCC; Hepatocellular carcinoma; IGF-1; Overall survival.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study was approved by the responsible ethics committee of the Medical Association of Rhineland Palatinate, Mainz, Germany. Written informed consent was obtained from all patients before enrolment.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
- Lee YH, Hsu CY, Chu CW, Liu PH, Hsia CY, Huang YH, Su CW, Chiou YY, Lin HC, Huo TI. A new Child-Turcotte-Pugh class 0 for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: determinants, prognostic impact and ability to improve the current staging systems. PLoS One. 2014;9(6):e99115. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0099115. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous