Mucinous Nevus
- PMID: 30065589
- PMCID: PMC6029955
- DOI: 10.5021/ad.2018.30.4.465
Mucinous Nevus
Abstract
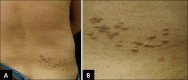
Mucinous nevus is an uncommon entity classified as either a cutaneous mucinosis or a connective tissue nevus. The condition presents as grouped papules and coalescent plaques growing in a unilateral or zosteriform manner. The key histopathological feature is a band-like deposition of mucin in the superficial dermis. A 34-year-old male presented with grouped gray-brown papules and confluent plaques exhibiting a zosteriform distribution on the right side of the lower back. The lesions had commenced in childhood. Histological examination revealed mucin deposition in the papillary dermis. Thus, we diagnosed a mucinous nevus. To date, only a few reports of such nevi have been reported in the literature. Therefore we report a rare case of mucinous nevus.
Keywords: Cutaneous; Mucin; Nevus.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST: The authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Redondo Bellón P, Vázquez-Doval J, Idoate M, Quintanilla E. Mucinous nevus. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1993;28:797–798. - PubMed
-
- Rongioletti F, Rebora A. Mucinous nevus. Arch Dermatol. 1996;132:1522–1523. - PubMed
-
- Cobos G, Braunstein I, Abuabara K, Chu EY, James W. Mucinous nevus: report of a case and review of the literature. JAMA Dermatol. 2014;150:1018–1019. - PubMed
-
- Tardío JC, Granados R. The cellular component of the mucinous nevus consists of CD34-positive fibroblasts. J Cutan Pathol. 2010;37:1019–1020. - PubMed
-
- Chi CC, Wang SH, Lin PY. Combined epidermal-connective tissue nevus of proteoglycan (a type of mucinous nevus): a case report and literature review. J Cutan Pathol. 2009;36:808–811. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

