Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Cirrhosis: A Review of Its Epidemiology, Risk Factors, Clinical Presentation, Diagnosis, Management, and Prognosis
- PMID: 30065915
- PMCID: PMC6051295
- DOI: 10.1155/2018/2784537
Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Cirrhosis: A Review of Its Epidemiology, Risk Factors, Clinical Presentation, Diagnosis, Management, and Prognosis
Abstract
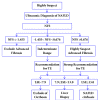
Cirrhosis is the common end stage of a number of chronic liver conditions and a significant cause of morbidity and mortality. With the growing epidemic of obesity and metabolic syndrome, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) has become the most common cause of chronic liver disease worldwide and will become one of the leading causes of cirrhosis. Increased awareness and understanding of NAFLD cirrhosis are essential. To date, there has been no published systematic review on NAFLD cirrhosis. Thus, this article reviews recent studies on the epidemiology, risk factors, clinical presentation, diagnosis, management, and prognosis of NAFLD cirrhosis.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical