Diagnosis and management of bone fragility in diabetes: an emerging challenge
- PMID: 30066131
- PMCID: PMC6267152
- DOI: 10.1007/s00198-018-4650-2
Diagnosis and management of bone fragility in diabetes: an emerging challenge
Abstract
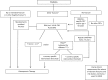
Fragility fractures are increasingly recognized as a complication of both type 1 and type 2 diabetes, with fracture risk that increases with disease duration and poor glycemic control. Yet the identification and management of fracture risk in these patients remains challenging. This review explores the clinical characteristics of bone fragility in adults with diabetes and highlights recent studies that have evaluated bone mineral density (BMD), bone microstructure and material properties, biochemical markers, and fracture prediction algorithms (i.e., FRAX) in these patients. It further reviews the impact of diabetes drugs on bone as well as the efficacy of osteoporosis treatments in this population. We finally propose an algorithm for the identification and management of diabetic patients at increased fracture risk.
Keywords: Diabetes; Diabetes-related bone disease; Fracture; Osteoporosis.
Conflict of interest statement
S Ferrari has received research grants, honoraria, and/or consultancies from Amgen, UCB, MSD, Labatec, Agnovos. B Abrahamsen has received research contracts with Novartis and UCB with funds paid to the institution. D Kendler has received research grants, honoraria, and/or consultancies from Amgen, Eli Lilly, AstraZeneca, Pfizer. R Eastell has received research grants from Alexion, Amgen Inc., and Ultragenyx, and consulting fees from Immunodiagnostic Systems, GlaxoSmithKline, and Amgen Inc. A Suzuki has received research grants and/or honoraria from Astellas, Chugai, Daiichi-Sankyo, Kyowa-Hakko Kirin, MSD, Novo Nordisk, Ono, Pfizer, Taisho Toyama, Tanabe-Mitsubishi and Takeda. R Josse has received consultancy fees and speaker honoraria from Amgen, Lilly, Merck. K Akesson has received lecture fees or consultancies from MSD, UCB, Amgen, Eli Lilly and Sandoz. A Schwartz has received a research grant from Hologic and consulting fees from Amgen. N Napoli has received consulting fees from Lilly and Amgen. G El-Hajj Fulehain, M Chandran, DD Pierroz, M Kraenzlin have no disclosure.
Figures
References
-
- International Diabetes Federation (2017) IDF diabetes atlas - Eighth Edition
-
- Vestergaard P, Rejnmark L, Mosekilde L. Relative fracture risk in patients with diabetes mellitus, and the impact of insulin and oral antidiabetic medication on relative fracture risk. Diabetologia. 2005;48:1292–1299. - PubMed
-
- Bonds DE, Larson JC, Schwartz AV, Strotmeyer ES, Robbins J, Rodriguez BL, Johnson KC, Margolis KL. Risk of fracture in women with type 2 diabetes: the Women's Health Initiative Observational Study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2006;91:3404–3410. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- MC_UP_A620_1015/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_U147585827/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_12011/2/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_U147585819/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_UP_A620_1014/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0601019/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/P020941/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0400491/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_U147585824/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 10/33/04/DH_/Department of Health/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_12011/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

