Paraneoplastic Sweet's syndrome
- PMID: 30066769
- PMCID: PMC6063096
- DOI: 10.1590/abd1806-4841.20187353
Paraneoplastic Sweet's syndrome
Abstract
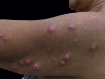
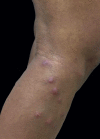
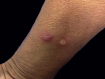
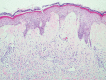
Sweet's syndrome is a rare dermatosis with little-known pathogenesis, associated with some clinical conditions such as infections, autoimmune diseases, inflammatory bowel diseases, vaccination, medications and neoplasms. Hematologic malignancies are the diseases most related to paraneoplastic Sweet's syndrome, but this clinical entity can also be found occasionally in some solid tumors, including genitourinary tract tumors. We report a rare case of paraneoplastic Sweet's syndrome associated with the diagnosis of cervical cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interests: None.
Figures
References
-
- Sweet RD. An acute febrile neutrophilic dermatosis. Br J Dermatol. 1964;76:349–356. - PubMed
-
- Raza S, Kirkland RS, Patel AA, Shortridge JR, Freter C. Insight into Sweet's syndrome and associated-malignancy: a review of the current literature. Int J Oncol. 2013;42:1516–1522. - PubMed
-
- Franco M, Giusti C, Malieni D, Ferrario D, Galimberti G, Parra IH. Sweet's syndrome associated with neoplasms. An Bras Dermatol. 2006;81:473–482.
-
- DeWitt CA, Buescher LS, Stone SP. Cutaneous manifestations of internal malignant disease: Cutaneous paraneoplastic syndromes. In: Wolff K, Goldsmith LA, Katz SI, Gilchrest B, Paller AS, Leffell DJ, editors. Fitzpatrick's Dermatology in General Medicine. 5th ed. NY: McGraw-Hill; 1999. pp. 2106–2120.
-
- Culp L, Crowder S, Hatch S. A rare association of Sweet's syndrome with cervical cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 2004;95:396–399. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

