A revised airway epithelial hierarchy includes CFTR-expressing ionocytes
- PMID: 30069044
- PMCID: PMC6295155
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-018-0393-7
A revised airway epithelial hierarchy includes CFTR-expressing ionocytes
Abstract
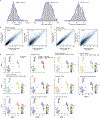
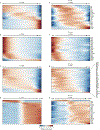
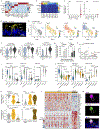
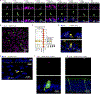
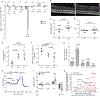
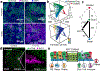
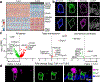
The airways of the lung are the primary sites of disease in asthma and cystic fibrosis. Here we study the cellular composition and hierarchy of the mouse tracheal epithelium by single-cell RNA-sequencing (scRNA-seq) and in vivo lineage tracing. We identify a rare cell type, the Foxi1+ pulmonary ionocyte; functional variations in club cells based on their location; a distinct cell type in high turnover squamous epithelial structures that we term 'hillocks'; and disease-relevant subsets of tuft and goblet cells. We developed 'pulse-seq', combining scRNA-seq and lineage tracing, to show that tuft, neuroendocrine and ionocyte cells are continually and directly replenished by basal progenitor cells. Ionocytes are the major source of transcripts of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator in both mouse (Cftr) and human (CFTR). Knockout of Foxi1 in mouse ionocytes causes loss of Cftr expression and disrupts airway fluid and mucus physiology, phenotypes that are characteristic of cystic fibrosis. By associating cell-type-specific expression programs with key disease genes, we establish a new cellular narrative for airways disease.
Figures









Comment in
-
Profile of an unknown airway cell.Nature. 2018 Aug;560(7718):313-314. doi: 10.1038/d41586-018-05813-7. Nature. 2018. PMID: 30097657 No abstract available.
-
Pulmonary Ionocytes Challenge the Paradigm in Cystic Fibrosis.Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2018 Oct;39(10):852-854. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2018.08.005. Epub 2018 Sep 10. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30213439
References
-
- Nunn’s Applied Respiratory Physiology −8th Edition. Available at: https://www.elsevier.com/books/nunns-applied-respiratory-physiology/lumb.... (Accessed: 5th April 2018)
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 DA047967/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK072482/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K08 HL131867/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K99 HL127181/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R00 HL127181/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK054759/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK047967/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R24 HL123482/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK043351/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL051670/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 ES005605/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- F31 HL136128/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 HL135816/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

