Verified iptables Firewall Analysis and Verification
- PMID: 30069072
- PMCID: PMC6044321
- DOI: 10.1007/s10817-017-9445-1
Verified iptables Firewall Analysis and Verification
Abstract
This article summarizes our efforts around the formally verified static analysis of iptables rulesets using Isabelle/HOL. We build our work around a formal semantics of the behavior of iptables firewalls. This semantics is tailored to the specifics of the filter table and supports arbitrary match expressions, even new ones that may be added in the future. Around that, we organize a set of simplification procedures and their correctness proofs: we include procedures that can unfold calls to user-defined chains, simplify match expressions, and construct approximations removing unknown or unwanted match expressions. For analysis purposes, we describe a simplified model of firewalls that only supports a single list of rules with limited expressiveness. We provide and verify procedures that translate from the complex iptables language into this simple model. Based on that, we implement the verified generation of IP space partitions and minimal service matrices. An evaluation of our work on a large set of real-world firewall rulesets shows that our framework provides interesting results in many situations, and can both help and out-compete other static analysis frameworks found in related work.
Keywords: Computer networks; Firewalls; Formal verification; Iptables; Isabelle; Netfilter; Semantics.
Figures



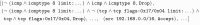


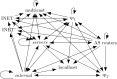
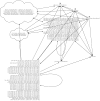
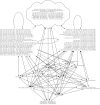
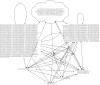
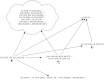
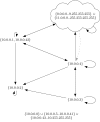
References
-
- Al-Shaer, E., Alsaleh, M.: ConfigChecker: a tool for comprehensive security configuration analytics. In: Configuration Analytics and Automation (SAFECONFIG), pp. 1–2. IEEE (2011). 10.1109/SafeConfig.2011.6111667
-
- Al-Shaer, E., Hamed, H.: Discovery of policy anomalies in distributed firewalls. In: Annual Joint Conference of the IEEE Computer and Communications Societies (INFOCOM), vol. 4, pp. 2605–2616 (2004). 10.1109/INFCOM.2004.1354680
-
- Analyzed firewall rulesets (raw data). https://github.com/diekmann/net-network. Accompanying material
-
- Anderson, C.J., Foster, N., Guha, A., Jeannin, J.B., Kozen, D., Schlesinger, C., Walker, D.: NetKAT: semantic foundations for networks. In: 41st ACM SIGPLAN-SIGACT Symposium on Principles of Programming Languages, POPL ’14, pp. 113–126. ACM, San Diego (2014). 10.1145/2535838.2535862
-
- Baker, F., Savola, P.: Ingress filtering for multihomed networks. RFC 3704 (Best Current Practice) (2004)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
