Intraoperative Electron Radiotherapy (IOERT) in the Treatment of Primary Breast Cancer
- PMID: 30069175
- PMCID: PMC6062668
- DOI: 10.1159/000489637
Intraoperative Electron Radiotherapy (IOERT) in the Treatment of Primary Breast Cancer
Abstract
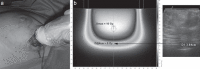
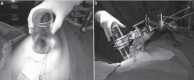
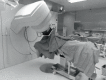
IOERT (intraoperative electron radiotherapy) in breast cancer is used either as a boost (10-12 Gy) followed by whole breast irradiation (WBI) or as full-dose partial breast irradiation (PBI, 20-24 Gy) during breast-conserving surgery. IOERT has the longest evidence of all IORT techniques. When administered as a boost, excellent low local recurrence rates were observed in long-term follow-up >5 years. Even in high-risk groups like triple-negative or locally advanced breast cancers, IOERT contributes to long-term local control rates of more than 90%. For selected low-risk groups, IOERT as PBI with 21 Gy seems to be a viable treatment alternative to standard WBI. IOERT has been shown to be advantageous for several reasons: Geographic misses are avoided due to direct visualization of the tumor bed; thus, a high single dose is delivered with utmost precision to small volumes, completely sparing the skin and ensuring good long-term cosmetic outcome. Furthermore, high single doses seem to induce biological mechanisms with verifiable antitumor capability in in-vitro cell-line studies. In addition, IOERT markedly shortens the overall treatment time both in combination with (now mostly hypofractionated) WBI or as a PBI in selected low-risk constellations.
Keywords: Boost; Breast cancer; Electrons; IOERT; Intraoperative electron radiotherapy; Tumor bed.
Figures

References
-
- Holland R, Veling SH, Mravunac M, et al. Histologic multifocality of Tis, T1–2 breast carcinomas. Implications for clinical trials of breast-conserving surgery. Cancer. 1985;56:979–990. - PubMed
-
- Faverly DR, Hendriks JH, Holland R. Breast carcinomas of limited extent: frequency, radiologic-pathologic characteristics, and surgical margin requirements. Cancer. 2001;91:647–659. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

