Fast Progressing His-Purkinje Conduction Disturbances in a Myotonic Dystrophy Pacient
- PMID: 30069244
- PMCID: PMC6060298
- DOI: 10.26574/maedica.2018.13.2.152
Fast Progressing His-Purkinje Conduction Disturbances in a Myotonic Dystrophy Pacient
Abstract
Myotonic dystrophy leads to multiple systemic complications and the age of death is earlier in myotonic dystrophy patients than in the general population. These patients have a high frequency of sudden death related to respiratory failure, cardiac arrhythmias and in particular to cardiac conduction disturbances. Prophylactic pacemaker implantation should be considered in asymptomatic myotonic dystrophy patients, which in the early stages of disease present minor conduction disturbances in 12-leads ECG. Even if the rate of progression of conduction abnormalities is usually slow, fast progression has been often observed thus making the clinical course of individual patients rather unpredictable.
Figures

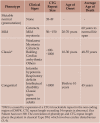
References
-
- Saba S, Vanderbrink BA, Luciano B, et al. Localization of the sites of conduction abnormalities in a mouse model of myotonic dystrophy. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 1999;10:1214–1220. - PubMed
-
- Groh WJ, Groh MR, Saha C, et al. Electrocardiographic abnormalities and sudden death in myotonic dystrophy type 1. N Engl J Med. 2008;25:2688–2697. - PubMed
-
- Melacini P, Villanova C, Menegazzo E, et al. Correlation between cardiac involvement and CTG trinucleotide repeat length in myotonic dystrophy. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1995;25:239–245. - PubMed
-
- Bird TD. Myotonic Dystrophy Type 1. Gene Reviews: September. 1999;
-
- Glover BM, Brugada P. Clinical Handbook of Cardiac Electrophysiology. Springer International Publishing Switzerland. . 2016;pp.:21–23.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
