Clinical Applications of Adiponectin Measurements in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Screening, Diagnosis, and Marker of Diabetes Control
- PMID: 30069271
- PMCID: PMC6057311
- DOI: 10.1155/2018/5187940
Clinical Applications of Adiponectin Measurements in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Screening, Diagnosis, and Marker of Diabetes Control
Abstract
Background: Adipose tissue-derived adiponectin has pleiotropic protective effects with suppression of inflammatory and metabolic derangements that may result in insulin resistance, metabolic syndrome, type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), and cardiovascular disease. The aim of this study was to evaluate adiponectin as a diagnostic marker of T2DM and diabetes control.
Methods: Fasting adiponectin, insulin, glucose, and HbA1c were determined in 376 patients with known T2DM and 575 subjects with undiagnosed diabetes but with family history of T2DM. Clinical and anthropometric data were recorded. Subjects were classified on the basis of degree of adiposity, insulin resistance (IR), and achievement of target HbA1c levels. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis was used to examine the diagnostic performance for undiagnosed DM.
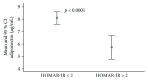
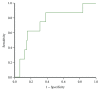
Results: In undiagnosed subjects, adiponectin was significantly lower in subjects with IR and diabetic subjects compared with those without. The area under the adiponectin ROC curve for diagnosis of DM was 0.740. In known T2DM subjects, those with good control had significantly higher adiponectin (8.6 versus 7.4 μg/mL) compared to subjects with poor control.
Conclusions: Adiponectin levels are associated with better glycemic control and could be a useful adjunct for screening for IR and T2DM. Therapeutic measures that increase adiponectin levels might be valuable targets for improving diabetes control and decreasing complications.
Figures
References
-
- Stefan N., Vozarova B., Funahashi T., et al. Plasma adiponectin concentration is associated with skeletal muscle insulin receptor tyrosine phosphorylation, and low plasma concentration precedes a decrease in whole-body insulin sensitivity in humans. Diabetes. 2002;51(6):1884–1888. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.51.6.1884. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical