Spoilage potential of psychrotrophic bacteria isolated from raw milk and the thermo-stability of their enzymes
- PMID: 30070086
- PMCID: PMC6102184
- DOI: 10.1631/jzus.B1700352
Spoilage potential of psychrotrophic bacteria isolated from raw milk and the thermo-stability of their enzymes
Abstract
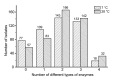
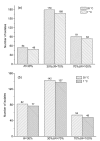
The storage and transportation of raw milk at low temperatures promote the growth of psychrotrophic bacteria and the production of thermo-stable enzymes, which pose great threats to the quality and shelf-life of dairy products. Though many studies have been carried out on the spoilage potential of psychrotrophic bacteria and the thermo-stabilities of the enzymes they produce, further detailed studies are needed to devise an effective strategy to avoid dairy spoilage. The purpose of this study was to explore the spoilage potential of psychrotrophic bacteria from Chinese raw milk samples at both room temperature (28 °C) and refrigerated temperature (7 °C). Species of Yersinia, Pseudomonas, Serratia, and Chryseobacterium showed high proteolytic activity. The highest proteolytic activity was shown by Yersinia intermedia followed by Pseudomonas fluorescens (d). Lipolytic activity was high in isolates of Acinetobacter, and the highest in Acinetobacter guillouiae. Certain isolates showed positive β-galactosidase and phospholipase activity. Strains belonging to the same species sometimes showed markedly different phenotypic characteristics. Proteases and lipases produced by psychrotrophic bacteria retained activity after heat treatment at 70, 80, or 90 °C, and proteases appeared to be more heat-stable than lipases. For these reasons, thermo-stable spoilage enzymes produced by a high number of psychrotrophic bacterial isolates from raw milk are of major concern to the dairy industry. The results of this study provide valuable data about the spoilage potential of bacterial strains in raw milk and the thermal resistance of the enzymes they produce.
Keywords: Spoilage enzyme; Psychrotrophic bacteria; Raw milk; Thermo-stability.
Conflict of interest statement
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Comparison of identification systems for psychrotrophic bacteria isolated from raw bovine milk.Int J Food Microbiol. 2014 Oct 17;189:26-38. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2014.07.023. Epub 2014 Jul 26. Int J Food Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 25113043
-
The main spoilage-related psychrotrophic bacteria in refrigerated raw milk.J Dairy Sci. 2018 Jan;101(1):75-83. doi: 10.3168/jds.2017-13069. Epub 2017 Nov 6. J Dairy Sci. 2018. PMID: 29102138
-
Pseudomonas spp. and Serratia liquefaciens as Predominant Spoilers in Cold Raw Milk.J Food Sci. 2015 Aug;80(8):M1842-9. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.12957. Epub 2015 Jul 17. J Food Sci. 2015. PMID: 26189559
-
Insights into Psychrotrophic Bacteria in Raw Milk: A Review.J Food Prot. 2019 Jul;82(7):1148-1159. doi: 10.4315/0362-028X.JFP-19-032. J Food Prot. 2019. PMID: 31225978 Review.
-
The Biodiversity of the Microbiota Producing Heat-Resistant Enzymes Responsible for Spoilage in Processed Bovine Milk and Dairy Products.Front Microbiol. 2017 Mar 1;8:302. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.00302. eCollection 2017. Front Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28298906 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Microbial Properties of Raw Milk throughout the Year and Their Relationships to Quality Parameters.Foods. 2022 Oct 4;11(19):3077. doi: 10.3390/foods11193077. Foods. 2022. PMID: 36230153 Free PMC article.
-
The Raw Milk Microbiota from Semi-Subsistence Farms Characteristics by NGS Analysis Method.Molecules. 2021 Aug 19;26(16):5029. doi: 10.3390/molecules26165029. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34443615 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Exocellobiohydrolase CBHA on Fermentation of Tobacco Leaves.J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024 Aug 28;34(8):1727-1737. doi: 10.4014/jmb.2404.04028. Epub 2024 Jun 19. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39049482 Free PMC article.
-
Cloning and characterization of an oxiranedicarboxylate hydrolase from Labrys sp. WH-1.J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2019 Dec.;20(12):995-1002. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B1900392. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2019. PMID: 31749346 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a real-time loop-mediated isothermal amplification method for monitoring Pseudomonas lurida in raw milk throughout the year of pasture.Front Microbiol. 2023 Apr 12;14:1133077. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1133077. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37125188 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baur C, Krewinkel M, Kutzli I, et al. Isolation and characterisation of a heat-resistant peptidase from Pseudomonas panacis withstanding general UHT processes. Int Dairy J. 2015;49:46–55. doi: 10.1016/j.idairyj.2015.04.009. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

