Therapeutic augmentation of ketogenic diet with a sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor in a super-refractory status epilepticus patient
- PMID: 30073144
- PMCID: PMC6068319
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ebcr.2018.05.002
Therapeutic augmentation of ketogenic diet with a sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor in a super-refractory status epilepticus patient
Abstract
Background: A ketogenic diet (KD) may have a role in treating patients in super-refractory status epilepticus (SRSE). Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors have a risk of ketoacidosis that could facilitate induction of KD.
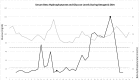
Case summary: A 42-year-old with a history of drug resistant epilepsy developed SRSE requiring several pharmacological interventions during her hospital course including the initiation of KD that failed. SGLT2 inhibitor therapy was initiated in a successful attempt to augment ketone production.
Conclusion: SGLT2 inhibitors may have a therapeutic value in SRSE patients who cannot achieve ketosis with KD alone.
Keywords: Epilepsy; Ketoacidosis; Ketogenic diet; Ketosis; Pentobarbital; Refractory status epilepticus; Seizure; Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor; Status epilepticus; Super-refractory status epilepticus.
Figures

References
-
- Hocker S.E., Britton J.W., Mandrekar J.N., Wijdicks E.F., Rabinstein A.A. Predictors of outcome in refractory status epilepticus. JAMA Neurol. 2013;70:72–77. - PubMed
-
- Ferlisi M., Shorvon S. The outcome of therapies in refractory and super-refractory convulsive status epilepticus and recommendations for therapy. Brain. 2012;135:2314–2328. - PubMed
-
- Hocker S., Tatum W.O., LaRoche S., Freeman W.D. Refractory and super-refractory status epilepticus: an update. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2014;14:452. - PubMed
-
- Brophy G.M., Bell R., Claassen J., Alldredger B., Bleck T.P., Glauser T. Guidelines for the evaluation and management of status epilepticus. Neurocrit Care. 2012;17:3–23. - PubMed
-
- Bodenant M., Moreau C., Sejourne C., Auvin S., Delval A., Cuisset J.M. Interest of the ketogenic diet in a refractory status epilepticus in adults. Rev Neurol. 2008;164:194–199. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

