A novel laser desorption/ionization method using through hole porous alumina membranes
- PMID: 30076645
- PMCID: PMC6175246
- DOI: 10.1002/rcm.8252
A novel laser desorption/ionization method using through hole porous alumina membranes
Abstract
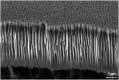
Rationale: A novel matrix-free laser desorption/ionization method based on porous alumina membranes was developed. The porous alumina membranes have a two-dimensional (2D) ordered structure consisting of closely aligned straight through holes of sub-micron in diameter that are amenable to mass production by industrial fabrication processes.
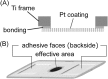
Methods: Considering a balance between the ion generating efficiency and the mechanical strength of the membranes, the typical values for the hole diameter, open aperture ratio and membrane thickness were set to 200 nm, 50% and 5 μm, respectively. The membranes were coated with platinum on a single side that was exposed to the laser. Evaluation experiments were conducted on the feasibility of this membrane structure for an ionization method using a single peptide and mixed peptides and polyethylene glycol samples and a commercial matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI) time-of-flight mass spectrometer in the positive ion mode.
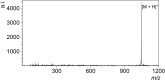
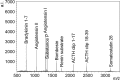
Results: Results showed a softness of ionization and no sweet spot nature. The capillary action of the through holes with very high aspect ratio enables several loading protocols including sample impregnation from the surface opposite to the laser exposure side.
Conclusions: The feasibility study indicates that the through hole porous alumina membranes have several advantages in terms of usefulness over the conventional surface-assisted laser desorption ionization (SALDI) methods. The proposed novel ionization method is termed Desorption Ionization Using Through Hole Alumina Membrane (DIUTHAME).
© 2018 The Authors Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Novel Blotting Method for Mass Spectrometry Imaging of Metabolites in Strawberry Fruit by Desorption/Ionization Using Through Hole Alumina Membrane.Foods. 2020 Apr 1;9(4):408. doi: 10.3390/foods9040408. Foods. 2020. PMID: 32244711 Free PMC article.
-
DIUTHAME enables matrix-free mass spectrometry imaging of frozen tissue sections.Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2020 May 15;34(9):e8729. doi: 10.1002/rcm.8729. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2020. PMID: 31951673
-
Quantitative analysis capability of DIUTHAME mass spectrometry verified by acetylcholinesterase enzyme-catalyzed reaction assays.J Mass Spectrom. 2022 Dec;57(12):e4895. doi: 10.1002/jms.4895. J Mass Spectrom. 2022. PMID: 36426802
-
Surface-assisted laser desorption ionization mass spectrometry techniques for application in forensics.Mass Spectrom Rev. 2015 Nov-Dec;34(6):627-40. doi: 10.1002/mas.21431. Epub 2014 Jun 11. Mass Spectrom Rev. 2015. PMID: 24916100 Review.
-
Negative ion laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometric analysis of small molecules by using nanostructured substrate as matrices.Mass Spectrom Rev. 2018 Sep;37(5):681-696. doi: 10.1002/mas.21558. Epub 2018 Mar 6. Mass Spectrom Rev. 2018. PMID: 29509966 Review.
Cited by
-
Mass Spectrometry Imaging.Mass Spectrom (Tokyo). 2022;11(1):A0102. doi: 10.5702/massspectrometry.A0102. Epub 2022 Feb 25. Mass Spectrom (Tokyo). 2022. PMID: 35291501 Free PMC article.
-
Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption and Electrospray Ionization Tandem Mass Spectrometry of Microbial and Synthetic Biodegradable Polymers.Polymers (Basel). 2023 May 18;15(10):2356. doi: 10.3390/polym15102356. Polymers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37242931 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Matrix-Free High-Resolution Atmospheric-Pressure SALDI Mass Spectrometry Imaging of Biological Samples Using Nanostructured DIUTHAME Membranes.Metabolites. 2021 Sep 15;11(9):624. doi: 10.3390/metabo11090624. Metabolites. 2021. PMID: 34564440 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Blotting Method for Mass Spectrometry Imaging of Metabolites in Strawberry Fruit by Desorption/Ionization Using Through Hole Alumina Membrane.Foods. 2020 Apr 1;9(4):408. doi: 10.3390/foods9040408. Foods. 2020. PMID: 32244711 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tanaka M, Waki H, Ido Y, Akita S, Yoshida T. Protein and polymer analyses up to m/z 100,000 by laser ionization time‐of‐flight mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 1988;2(8):151‐153.
-
- Sunner J, Dratz E, Chen YC. Graphite surface‐assisted laser desorption/ionization time‐of‐flight mass spectrometry of peptides and proteins from liquid solutions. Anal Chem. 1995;67(23):4335‐4342. - PubMed
-
- Dale MJ, Knochenmuss R, Zenobi R. Graphite/liquid mixed matrices for laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry. Anal Chem. 1996;68(19):3321‐3329. - PubMed
-
- Dale MJ, Knochenmuss R, Zenobi R. Two‐phase matrix‐assisted laser desorption/ionization: Matrix selection and sample pretreatment for complex anionic analytes. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 1997;11(1):136‐142.
-
- Chen YC, Shiea J, Sunner J. Thin‐layer chromatography‐mass spectrometry using activated carbon surface‐assisted laser desorption/ionization. J Chromatogr A. 1998;826(1):77‐86. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
