Similarities and differences in surface receptor expression by THP-1 monocytes and differentiated macrophages polarized using seven different conditioning regimens
- PMID: 30077333
- PMCID: PMC7611637
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2018.07.008
Similarities and differences in surface receptor expression by THP-1 monocytes and differentiated macrophages polarized using seven different conditioning regimens
Abstract
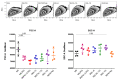
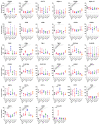
Macrophages are key in orchestrating immune responses to micro-environmental stimuli, sensed by a complex set of surface receptors. The human cell line THP-1 has a monocytic phenotype, including the ability to differentiate into macrophages, providing a tractable, standardised surrogate for human monocyte-derived macrophages. Here we assessed the expression of 49 surface markers including Fc, complement, C-type lectin and scavenger receptors; TIMs; Siglecs; and co-stimulatory molecules by flow cytometry on both THP-1 monocytes and macrophages and following macrophage activation with seven standard conditioning/polarizing stimuli. Of the 34 surface markers detected on macrophages, 18 altered expression levels on activation. From these, expression of 9 surface markers were consistently altered by all conditioning regimens, while 9 were specific to individual polarizing stimuli. This study provides a resource for the study of macrophages and highlights that macrophage polarization states share much in common and the differences do not easily fit a simple classification system.
Keywords: Cell surface; Flow cytometry; Macrophage; Monocyte; Polarization; THP-1.
Copyright © 2018. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Martinez FO, Sica A, Mantovani A, Locati M. Macrophage activation and polarization, Front. Biosci. 2008:453–461. - PubMed
-
- Boyle JJ, Johns M, Kampfer T, Nguyen AT, Game L, Schaer DJ, Mason JC, Haskard DO. Activating transcription factor 1 directs Mhem atheroprotective macrophages through coordinated iron handling and foam cell protection. Circ Res. 2012;1:20–33. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

