Antibacterial effects and resistance induction of silver and gold nanoparticles against Staphylococcus aureus-induced mastitis and the potential toxicity in rats
- PMID: 30079629
- PMCID: PMC6460268
- DOI: 10.1002/mbo3.698
Antibacterial effects and resistance induction of silver and gold nanoparticles against Staphylococcus aureus-induced mastitis and the potential toxicity in rats
Abstract
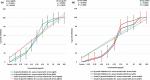
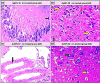
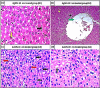
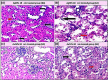
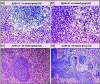
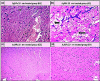
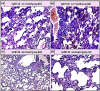
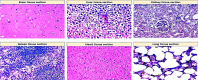
Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) is one of the prevalent mastitis-inducing pathogens worldwide. The resistance of S. aureus to antibiotics is a common issue for dairy farms. Recently, nanoparticles (NPs) have been used for treating antibiotic-resistant bacteria. We therefore aimed to investigate the antimicrobial effect of silver and gold NPs (AgNPs and AuNPs, respectively) and the resistance developed by S. aureus as well as the toxic effects of both NPs in rats. We used 198 S. aureus strains to determine the antibacterial effects of AgNPs and AuNPs. The microdilution method was used to establish the minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) of both NPs. To induce resistance, 20 S. aureus strains were passaged 10 times in broth medium with sublethal doses of NPs and an additional 10 times without NPs to examine the stability of resistance. Histopathology was performed after oral administration to the rats with the study doses of 0.25, 0.5, 1, and 2 mg/kg of NPs for 30 days. The MICs of 10-nm AgNPs, 20-nm AgNPs, 10-nm AuNPs, and 20-nm AuNPs against S. aureus were 14.70 ± 1.19 μg/ml, 9.15 ± 0.13 μg/ml, 24.06 ± 2.36 μg/ml, and 18.52 ± 1.26 μg/ml, respectively. Most strains developed strong resistance when treated with 20-nm or 10-nm AgNPs, whereas only two strains were resistant to 10-nm AuNPs and three strains to 20-nm AuNPs. No cross-resistance between NPs and various antibiotics was identified in any of the adapted S. aureus strains. Organ histopathology revealed that 0.25, 0.5, and 1 mg/kg doses of AgNPs and AuNPs were not toxic to rat tissue. In contrast, a higher dose (2 mg/kg) of NPs impaired all organs tested. This study demonstrates the antibacterial effects of NPs. S. aureus strains develop resistance less frequently against AuNPs than AgNPs, and neither AuNPs nor AgNPs was toxic to rats at low doses.
Keywords: Staphylococcus aureus; antibacterial; nanoparticles; resistance induction; toxicity.
© 2018 The Authors. MicrobiologyOpen published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Ali, D. M. , Thajuddin, N. , Jeganathan, K. , & Gunasekaran, M. (2011). Plant extract mediated synthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles and its antibacterial activity against clinically isolated pathogens. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 2, 360–365. - PubMed
-
- Benić, M. H. , Habrun, B. , & Kompes, G. (2012). Clinical and epidemiological aspects of cow mastitis caused by Staphylococcus aureus and its methicillin‐resistant strains. Journal of Medical Sciences, 37, 113–121.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

