The Relationship Between Optic Disc Volume, Area, and Frisén Score in Patients With Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension
- PMID: 30081012
- PMCID: PMC6214729
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajo.2018.07.032
The Relationship Between Optic Disc Volume, Area, and Frisén Score in Patients With Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension
Abstract
Purpose: To compare measurements of papilledema using fundus photography, optical coherence tomography (OCT), and Frisén score in patients with idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH).
Design: Retrospective, noncomparative analysis of randomized controlled trial data.
Methods: The Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension Treatment Trial (IIHTT) evaluated weight management and treatment with acetazolamide compared with placebo in patients with IIH and mild visual loss. Among the 126 subjects in the IIHTT OCT substudy, fundus photographs and OCT scans of the optic disc were taken at baseline and at 6 and 12 months after enrollment. Trained readers scored each eye using a modified Frisén scale and measured the area of disc elevation. OCT scans assessed optic nerve head (ONH) volume. Correlations between volume and area were computed for both study and nonstudy eyes.
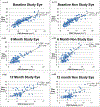
Results: Disc area and ONH volume were positively correlated at baseline (R2 = 0.77 in study eyes, P < .001). Correlations between area and volume were similar in the treatment groups at baseline, but were weaker in the acetazolamide group compared with the placebo group at 6 months (R2 = 0.25 vs R2 = 0.76 in study eyes) and 12 months (R2 = 0.19 vs R2 = 0.65 in study eyes). At 6 and 12 months after enrollment, there was no consistent relationship between Frisén score, disc area, and ONH volumes in the acetazolamide group.
Conclusion: Frisén score fails to reflect the photographic area and OCT volume of papilledema after treatment with acetazolamide. Clinicians should use caution when using the Frisén scale to monitor the effect of treatment on papilledema over time.
Copyright © 2018 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Friedman DI, Jacobson DM. Diagnostic criteria for idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Neurology 2002;59(10):1492–1495. - PubMed
-
- Smith JL. Whence pseudotumor cerebri? J Clin Neuroophthalmol 1985;5(1):55–56. - PubMed
-
- Wall M, George D. Idiopathic intracranial hypertension. A prospective study of 50 patients. Brain 1991;114 ( Pt 1A):155–180. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

