Recommendations for Improving the Quality of Rare Disease Registries
- PMID: 30081484
- PMCID: PMC6121483
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph15081644
Recommendations for Improving the Quality of Rare Disease Registries
Abstract
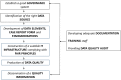
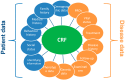
Rare diseases (RD) patient registries are powerful instruments that help develop clinical research, facilitate the planning of appropriate clinical trials, improve patient care, and support healthcare management. They constitute a key information system that supports the activities of European Reference Networks (ERNs) on rare diseases. A rapid proliferation of RD registries has occurred during the last years and there is a need to develop guidance for the minimum requirements, recommendations and standards necessary to maintain a high-quality registry. In response to these heterogeneities, in the framework of RD-Connect, a European platform connecting databases, registries, biobanks and clinical bioinformatics for rare disease research, we report on a list of recommendations, developed by a group of experts, including members of patient organizations, to be used as a framework for improving the quality of RD registries. This list includes aspects of governance, Findable, Accessible, Interoperable and Reusable (FAIR) data and information, infrastructure, documentation, training, and quality audit. The list is intended to be used by established as well as new RD registries. Further work includes the development of a toolkit to enable continuous assessment and improvement of their organizational and data quality.
Keywords: patient registry; quality; rare diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- The Council of the European Union Council Recommendation of 8 June 2009 on an Action in the Field of Rare Diseases (2009/C 151/02) Off. J. Eur. Union. 2009;C151:7–10.
-
- Directive 2011/24/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council of 9 March 2011 on the Application of Patients’ Rights in Cross-Border Healthcare. Off. J. Eur. Union. 2011;L88:45–65.
-
- Orphanet Report Series-Rare Disease Registries in Europe—May 2018. [(accessed on 20 June 2018)]; Available online: http://www.orpha.net/orphacom/cahiers/docs/GB/Registries.pdf.
-
- RD-Connect. [(accessed on 19 June 2018)]; Available online: https://rd-connect.eu/
-
- Guidelines for Data Sources and Quality for RD Registries in Europe. [(accessed on 20 June 2018)]; Available online: http://www.epirare.eu/del.html.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous