Diabetic nephropathy and hypertension in diabetes patients of sub-Saharan countries: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 30081966
- PMCID: PMC6080368
- DOI: 10.1186/s13104-018-3670-5
Diabetic nephropathy and hypertension in diabetes patients of sub-Saharan countries: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Objective: This meta-analysis was undertaken to estimate the prevalence of diabetic nephropathy and its association with hypertension in diabetics of sub-Saharan African countries.
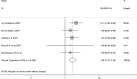
Results: A total of 27 studies were included for the meta-analysis. The pooled overall prevalence of diabetic nephropathy was 35.3 (95% CI 27.46-43.14). In sub-group analyses by types of diabetes and regions, for instance, the prevalence was 41.4% (95% CI 32.2-50.58%) in type-2 diabetes mellitus and 29.7% (95% CI 14.3-45.1%) in Eastern Africa. Pooled point estimates from included studies revealed an increased risk of diabetic nephropathy with hypertension compared to without hypertension (OR = 1.67, 95% CI 1.31, 2.14). Diabetic nephropathy is a common complication in diabetic patients. Diabetic nephropathy complication is significantly higher in hypertensive patients. A preventive strategy should be adopted or planned to reduce diabetes mellitus and its complication of neuropathy, particularly in hypertensive.
Keywords: Diabetic nephropathy; Hypertension; Sub-Saharan countries.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prevalence and Genotype Distribution of High-Risk Human Papillomavirus Infection Among Sub-Saharan African Women: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Public Health. 2022 Jul 8;10:890880. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.890880. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35875040 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic review on urine albumin testing for early detection of diabetic complications.Health Technol Assess. 2005 Aug;9(30):iii-vi, xiii-163. doi: 10.3310/hta9300. Health Technol Assess. 2005. PMID: 16095545
-
Dengue Virus Infection in Sub-Saharan Africa Between 2010 and 2020: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021 May 25;11:678945. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.678945. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34113579 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of Rickettsia africae in tick vectors collected from mammalian hosts in sub-Saharan Africa: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2022 Jul;13(4):101960. doi: 10.1016/j.ttbdis.2022.101960. Epub 2022 Apr 26. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2022. PMID: 35537238
-
Efficacy of low-protein diet for diabetic nephropathy: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials.Lipids Health Dis. 2018 Jun 19;17(1):141. doi: 10.1186/s12944-018-0791-8. Lipids Health Dis. 2018. PMID: 29914534 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Prevalence and predictors of chronic kidney disease among type 2 diabetic patients worldwide, systematic review and meta-analysis.Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2023 Nov 28;15(1):245. doi: 10.1186/s13098-023-01202-x. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2023. PMID: 38012781 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of potential therapeutic target genes in mouse mesangial cells associated with diabetic nephropathy using bioinformatics analysis.Exp Ther Med. 2019 Jun;17(6):4617-4627. doi: 10.3892/etm.2019.7524. Epub 2019 Apr 23. Exp Ther Med. 2019. PMID: 31105790 Free PMC article.
-
Incidence and Predictors of Chronic Kidney Disease among Diabetes Mellitus Patients: A Retrospective Follow-Up Study at a Tertiary Health-Care Setting of Ethiopia.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2021 Oct 28;14:4381-4390. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S335572. eCollection 2021. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2021. PMID: 34737594 Free PMC article.
-
Identify the co-expressed genes of hypertensive nephropathy and diabetic nephropathy.Sci Rep. 2025 Jun 3;15(1):19418. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-04679-w. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40461634 Free PMC article.
-
Metformin-Insulin versus Metformin-Sulfonylurea Combination Therapies in Type 2 Diabetes: A Comparative Study of Glycemic Control and Risk of Cardiovascular Diseases in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2021 Jul 24;14:3345-3359. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S312997. eCollection 2021. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2021. PMID: 34335036 Free PMC article.
References
-
- CfDCaPNDS Report. Estimates of diabetes and its burden in the United States. Atlanta: US Department of Health and Human Services; 2014.
-
- Cosgrove P, Engelgau M, Islam I. Cost-effective approaches to diabetes care and prevention. Diabetes Voice. 2002;47(4):13–17.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical