Diabetic nephropathy and hypertension in diabetes patients of sub-Saharan countries: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 30081966
- PMCID: PMC6080368
- DOI: 10.1186/s13104-018-3670-5
Diabetic nephropathy and hypertension in diabetes patients of sub-Saharan countries: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Objective: This meta-analysis was undertaken to estimate the prevalence of diabetic nephropathy and its association with hypertension in diabetics of sub-Saharan African countries.
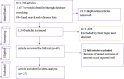
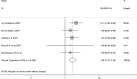
Results: A total of 27 studies were included for the meta-analysis. The pooled overall prevalence of diabetic nephropathy was 35.3 (95% CI 27.46-43.14). In sub-group analyses by types of diabetes and regions, for instance, the prevalence was 41.4% (95% CI 32.2-50.58%) in type-2 diabetes mellitus and 29.7% (95% CI 14.3-45.1%) in Eastern Africa. Pooled point estimates from included studies revealed an increased risk of diabetic nephropathy with hypertension compared to without hypertension (OR = 1.67, 95% CI 1.31, 2.14). Diabetic nephropathy is a common complication in diabetic patients. Diabetic nephropathy complication is significantly higher in hypertensive patients. A preventive strategy should be adopted or planned to reduce diabetes mellitus and its complication of neuropathy, particularly in hypertensive.
Keywords: Diabetic nephropathy; Hypertension; Sub-Saharan countries.
Figures
References
-
- CfDCaPNDS Report. Estimates of diabetes and its burden in the United States. Atlanta: US Department of Health and Human Services; 2014.
-
- Cosgrove P, Engelgau M, Islam I. Cost-effective approaches to diabetes care and prevention. Diabetes Voice. 2002;47(4):13–17.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical