Microglial translational profiling reveals a convergent APOE pathway from aging, amyloid, and tau
- PMID: 30082275
- PMCID: PMC6122978
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20180653
Microglial translational profiling reveals a convergent APOE pathway from aging, amyloid, and tau
Abstract
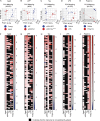
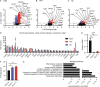
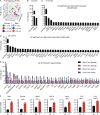
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is an age-associated neurodegenerative disease characterized by amyloidosis, tauopathy, and activation of microglia, the brain resident innate immune cells. We show that a RiboTag translational profiling approach can bypass biases due to cellular enrichment/cell sorting. Using this approach in models of amyloidosis, tauopathy, and aging, we revealed a common set of alterations and identified a central APOE-driven network that converged on CCL3 and CCL4 across all conditions. Notably, aged females demonstrated a significant exacerbation of many of these shared transcripts in this APOE network, revealing a potential mechanism for increased AD susceptibility in females. This study has broad implications for microglial transcriptomic approaches and provides new insights into microglial pathways associated with different pathological aspects of aging and AD.
© 2018 Kang et al.
Figures


References
-
- Austermann J., Friesenhagen J., Fassl S.K., Petersen B., Ortkras T., Burgmann J., Barczyk-Kahlert K., Faist E., Zedler S., Pirr S., et al. . 2014. Alarmins MRP8 and MRP14 induce stress tolerance in phagocytes under sterile inflammatory conditions. Cell Reports. 9:2112–2123. 10.1016/j.celrep.2014.11.020 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cook C., Kang S.S., Carlomagno Y., Lin W.L., Yue M., Kurti A., Shinohara M., Jansen-West K., Perkerson E., Castanedes-Casey M., et al. . 2015. Tau deposition drives neuropathological, inflammatory and behavioral abnormalities independently of neuronal loss in a novel mouse model. Hum. Mol. Genet. 24:6198–6212. 10.1093/hmg/ddv336 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Corneveaux J.J., Myers A.J., Allen A.N., Pruzin J.J., Ramirez M., Engel A., Nalls M.A., Chen K., Lee W., Chewning K., et al. . 2010. Association of CR1, CLU and PICALM with Alzheimer’s disease in a cohort of clinically characterized and neuropathologically verified individuals. Hum. Mol. Genet. 19:3295–3301. 10.1093/hmg/ddq221 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

