Patient-physician gender concordance and increased mortality among female heart attack patients
- PMID: 30082406
- PMCID: PMC6112736
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1800097115
Patient-physician gender concordance and increased mortality among female heart attack patients
Abstract
We examine patient gender disparities in survival rates following acute myocardial infarctions (i.e., heart attacks) based on the gender of the treating physician. Using a census of heart attack patients admitted to Florida hospitals between 1991 and 2010, we find higher mortality among female patients who are treated by male physicians. Male patients and female patients experience similar outcomes when treated by female physicians, suggesting that unique challenges arise when male physicians treat female patients. We further find that male physicians with more exposure to female patients and female physicians have more success treating female patients.
Keywords: gender disparity; heart attacks; mortality; patient advocacy; patient–physician gender concordance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
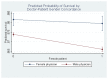
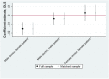
References
-
- Cohen PN, Huffman ML. Working for the woman? Female managers and the gender wage gap. Am Sociol Rev. 2007;72:681–704.
-
- Cohen LE, Broschak JP, Haveman HA. And then there were more? The effect of organizational sex composition on the hiring and promotion of managers. Am Sociol Rev. 1998;63:711–727.
-
- Carrell SE, Page ME, West JE. Sex and science: How professor gender perpetuates the gender gap. Q J Econ. 2010;125:1101–1144.
-
- Knepper M. When the shadow is the substance: Judge gender and the outcomes of workplace sex discrimination cases. J Labor Econ. 2017;36:623–664.
-
- Kudenchuk PJ, Maynard C, Martin JS, Wirkus M, Weaver WD. Comparison of presentation, treatment, and outcome of acute myocardial infarction in men versus women (the Myocardial Infarction Triage and Intervention Registry) Am J Cardiol. 1996;78:9–14. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

