FGF18, a prominent player in FGF signaling, promotes gastric tumorigenesis through autocrine manner and is negatively regulated by miR-590-5p
- PMID: 30082912
- PMCID: PMC6318220
- DOI: 10.1038/s41388-018-0430-x
FGF18, a prominent player in FGF signaling, promotes gastric tumorigenesis through autocrine manner and is negatively regulated by miR-590-5p
Abstract
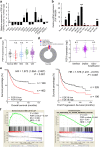
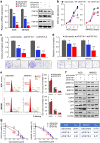
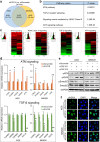
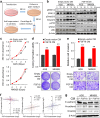
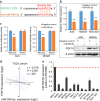
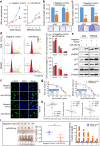
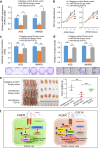
Fibroblast growth factors (FGFs) and their receptors are significant components during fundamental cellular processes. FGF18 plays a distinctive role in modulating the activity of both tumor cells and tumor microenvironment. This study aims to comprehensively investigate the expression and functional role of FGF18 in gastric cancer (GC) and elucidate its regulatory mechanisms. The upregulation of FGF18 was detected in seven out of eleven (63.6%) GC cell lines. In primary GC samples, FGF18 was overexpressed in genomically stable and chromosomal instability subtypes of GC and its overexpression was associated with poor survival. Knocking down FGF18 inhibited tumor formation abilities, induced G1 phase cell cycle arrest and enhanced anti-cancer drug sensitivity. Expression microarray profiling revealed that silencing of FGF18 activated ATM pathway but quenched TGF-β pathway. The key factors that altered in the related signaling were validated by western blot and immunofluorescence. Meanwhile, treating GC cells with human recombinant FGF18 or FGF18-conditioned medium accelerated tumor growth through activation of ERK-MAPK signaling. FGF18 was further confirmed to be a direct target of tumor suppressor, miR-590-5p. Their expressions showed a negative correlation in primary GC samples and more importantly, re-overexpression of FGF18 partly abolished the tumor-suppressive effect of miR-590-5p. Our study not only identified that FGF18 serves as a novel prognostic marker and a therapeutic target in GC but also enriched the knowledge of FGF-FGFR signaling during gastric tumorigenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

