Morphological diversity and connectivity of hippocampal interneurons
- PMID: 30084021
- PMCID: PMC6132631
- DOI: 10.1007/s00441-018-2882-2
Morphological diversity and connectivity of hippocampal interneurons
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Morphological diversity and connectivity of hippocampal interneurons.Cell Tissue Res. 2019 Jun;376(3):485-486. doi: 10.1007/s00441-019-03014-w. Cell Tissue Res. 2019. PMID: 30945003 Free PMC article.
Abstract
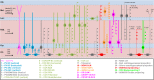
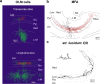
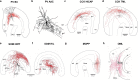
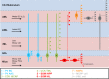
The mammalian forebrain is constructed from ensembles of neurons that form local microcircuits giving rise to the exquisite cognitive tasks the mammalian brain can perform. Hippocampal neuronal circuits comprise populations of relatively homogenous excitatory neurons, principal cells and exceedingly heterogeneous inhibitory neurons, the interneurons. Interneurons release GABA from their axon terminals and are capable of controlling excitability in every cellular compartment of principal cells and interneurons alike; thus, they provide a brake on excess activity, control the timing of neuronal discharge and provide modulation of synaptic transmission. The dendritic and axonal morphology of interneurons, as well as their afferent and efferent connections within hippocampal circuits, is central to their ability to differentially control excitability, in a cell-type- and compartment-specific manner. This review aims to provide an up-to-date compendium of described hippocampal interneuron subtypes, with respect to their morphology, connectivity, neurochemistry and physiology, a full understanding of which will in time help to explain the rich diversity of neuronal function.
Keywords: Connectivity; GABA; Hippocampus; Interneuron; Morphology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Acsády L, Arabadzisz D, Freund TF. Correlated morphological and neurochemical features identify different subsets of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide-immunoreactive interneurons in rat hippocampus. Neuroscience. 1996;73:299–315. - PubMed
-
- Acsády L, Görcs T, Freund T. Different populations of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide-immunoreactive interneurons are specialized to control pyramidal cells or interneurons in the hippocampus. Neuroscience. 1996;73:317–334. - PubMed
-
- Ali AB. Presynaptic inhibition of GABAA receptor-mediated unitary IPSPs by cannabinoid receptors at synapses between CCK-positive interneurons in rat hippocampus. J Neurophysiol. 2007;98:861–869. - PubMed
-
- Ali A, Todorova M. Asynchronous release of GABA via tonic cannabinoid receptor activation at identified interneuron synapses in rat CA1. Eur J Neurosci. 2010;31:1196–1207. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

