The Rb tumor suppressor regulates epithelial cell migration and polarity
- PMID: 30084175
- PMCID: PMC6168347
- DOI: 10.1002/mc.22886
The Rb tumor suppressor regulates epithelial cell migration and polarity
Abstract
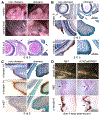
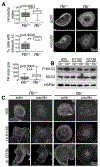
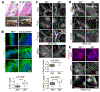
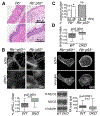
Altered cell polarity and migration are hallmarks of cancer and metastases. Here we show that inactivation of the retinoblastoma gene (Rb) tumor suppressor causes defects in tissue closure that reflect the inability of Rb null epithelial cells to efficiently migrate and polarize. These defects occur independently of pRB's anti-proliferative role and instead correlate with upregulation of RhoA signaling and mislocalization of apical-basal polarity proteins. Notably, concomitant inactivation of tp53 specifically overrides the motility defect, and not the aberrant polarity, thereby uncovering previously unappreciated mechanisms by which Rb and tp53 mutations cooperate to promote cancer development and metastases.
Keywords: PAR complex; RhoA Rock signaling; aPKC; eyes open phenotype; planar cell polarity.
© 2018 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Ridley AJ. Rho family proteins: coordinating cell responses. Trends Cell Biol 2001;11(12):471–477. - PubMed
-
- Etienne-Manneville S, Hall A. Cell polarity: Par6, aPKC and cytoskeletal crosstalk. Curr Opin Cell Biol 2003;15(1):67–72. - PubMed
-
- Vega FM, Ridley AJ. Rho GTPases in cancer cell biology. FEBS Lett 2008;582(14):2093–2101. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

